ADD-ONS / MEDICATION / ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY
Fondaparinux (ARIXTRA)
Updated on 03/10/2024, published on 24/01/2022
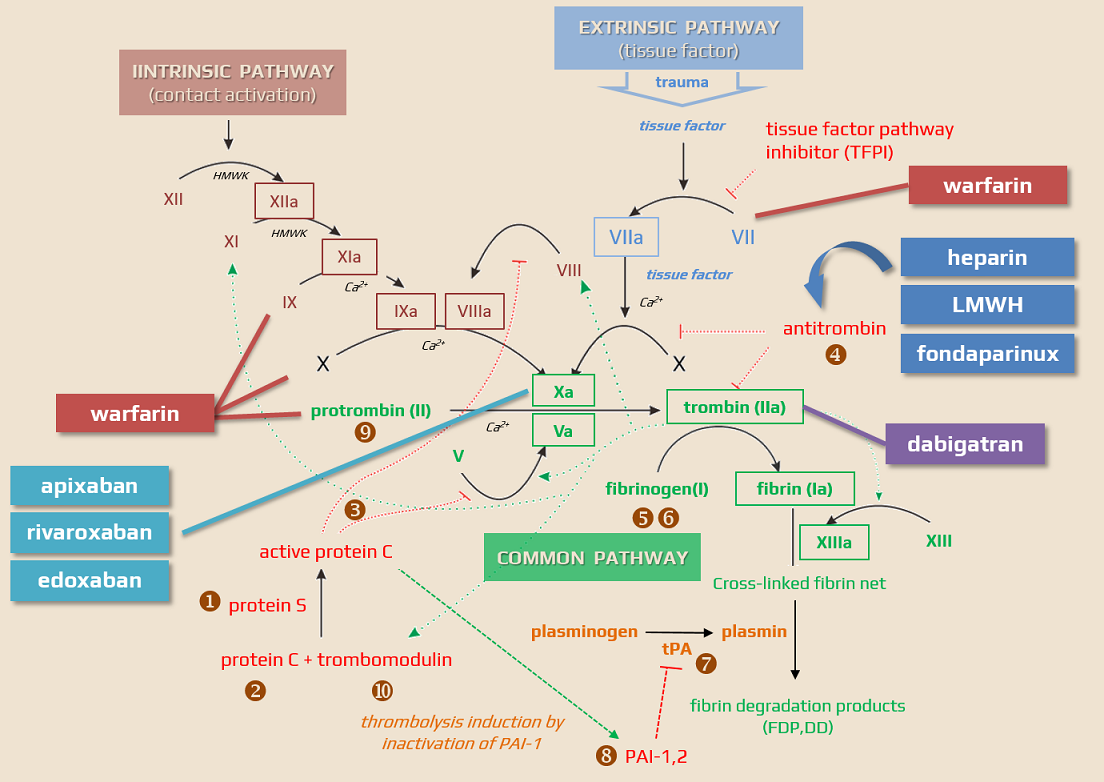
- fondaparinux is a synthetic pentasaccharide that acts as an indirect factor Xa inhibitor (by binding to antithrombin)
- it is administered subcutaneously (SC) and appears to be more effective than enoxaparin in preventing VTE without the increased risk of bleeding
- advantage of fondaparinux over LMWH or unfractionated heparin (UFH) is significantly lower risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
Pharmacodynamics
- fondaparinux selectively and indirectly (by binding to antithrombin) inhibits factor Xa ⇒ inhibition of thrombin generation [Turpie, 2008]
- does not affect prothrombin or platelets
- after activating antithrombin III (AT III) and increasing its natural ability to inactivate FXa, fondaparinux is released from the AT III/FXa complex and can activate other antithrombin molecules
- affects only factor X (compared to LMWH/heparin, it lacks the longer carbohydrate chain required to bind to thrombin)
- at a dose of 2.5 mg, fondaparinux does not affect common coagulation tests such as activated partial thrombin time (aPTT), activated clotting time (ACT) or prothrombin time (PT)/international normalized ratio (INR) plasma tests, or bleeding time or fibrinolytic activity
- rarely, increased aPTT was reported
Pharmacokinetics
- it is administered subcutaneously with a rapid and complete absorption
- the pharmacokinetics are linear; it does not bind to monocyte-macrophage cells, platelets (PF4), endothelium, or plasma proteins
- after a dose of 2.5 mg, a maximum concentration of 0.39-0.5 mg/L is reached in 3 hours
- excreted by the kidneys – with normal renal function, the majority of fondaparinux is eliminated unchanged in the urine (77% within 72 hours after administration), and the elimination half-life is 17-21 hours (longer than for UFH/LMWH)
- excretion is prolonged in patients with renal impairment:
- 25% decrease in mild renal insufficiency
- creatinine clearance of 30-50 mL/min – excretion decreased by 40%
- creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min – excretion decreased by > 50%
- elimination is further prolonged:
- at age > 75 years approx. by 25 %
- in patients weighing < 50 kg
- at age > 75 years approx. by 25 %
- does not affect fibrinogen levels but increases protein S (PS) activity
- does not induce the antibodies production (heparin/particle factor 4 type) or thrombocytopenia
- can be administered during pregnancy
- based on limited experience, it can be considered safe and may be an alternative for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic disease when LMWH (which is the drug of the first choice) cannot be used
Interactions
- the concomitant use of oral anticoagulants (warfarin), platelet inhibitors (acetylsalicylic acid), NSAIDs (piroxicam), and digoxin does not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of fondaparinux sodium
- fondaparinux neither influences the pharmacodynamics of warfarin, acetylsalicylic acid, piroxicam, and digoxin
- agents that may increase the risk of bleeding should be discontinued prior to initiation of therapy with fondaparinux unless these agents are essential
- if coadministration is necessary, patients should be monitored closely for bleeding
- if coadministration is necessary, patients should be monitored closely for bleeding
- fondaparinux sodium does not significantly bind to plasma proteins other than AT III ⇒ no drug interactions by protein-binding displacement are expected
Indications
- VTE prevention during orthopedic procedures on the lower extremities (hip fracture surgery, hip or knee replacement)
- VTE prevention patients undergoing abdominal surgery who are expected to be at high risk of thromboembolic complications
- treatment of acute symptomatic spontaneous thrombophlebitis
- treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in adult patients, except in hemodynamically unstable patients or patients requiring thrombolysis or pulmonary embolectomy
- off-label indications
- DVT prophylaxis in medically ill (including cancer patients), who are considered to be at increased risk of VTE
- DVT prophylaxis in patients with a history of heparin–induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
- treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
- no affinity to PF4
- anticoagulation during a non–ST–segment–elevation myocardial infarction (non–STEMI)
Contraindications
- severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min)
- active clinically significant bleeding
- bacterial endocarditis
- known hypersensitivity to fondaparinux (e.g., angioedema, anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions)
- thrombocytopenia associated with a positive in vitro test for anti-platelet antibody in the presence of fondaparinux
- body weight <50 kg (for VTE prophylaxis only)
Dosing
Neutralization of the effect
- canceling the effect of fondaparinux is difficult, as with LMWH, because a specific antidote is not available
- in cases of fondaparinux-related hemorrhage, consider coagulation factors supplementation (limited clinical data) → Neutralization of anticoagulant effect
Monitoring
- fondaparinux anti-Xa assay can be used to monitor fondaparinux therapy
- it measures the inhibitory effect of the fondaparinux-AT complex on FXa
- an optical method based on the principle of chromogenic substrates without the addition of exogenous antithrombin
- the analysis depends on the amount of AT in the plasma
- sampling should be drawn 3-4 hours after drug administration when the highest anti-Xa activity is reached (peak steady-state plasma concentration)
- prophylactic dose 2.5 mg SC once daily … 0.39 – 0.50 mg/L (μg/mL)
- therapeutic dose 7.5 mg SC once daily … 1.2 – 1.26 mg/L (μg/mL)
- prophylactic dose 2.5 mg SC once daily … 0.39 – 0.50 mg/L (μg/mL)
Complications
- most common adverse events include:
- bleeding
- chest pain
- confusion, convulsions
- arrhythmia
- numbness or tingling in extremities


