ADD-ONS / SCALES
FAZEKAS scale
Updated on 22/04/2024, published on 20/02/2023
- a scoring system for simple assessment of white matter lesions (WML) on brain MRI scans was proposed by Fazekas in 1987 (Fazekas, 1987)
- WMLs often result from arteriolosclerosis (arteriolopathy)
- WMLs often result from arteriolosclerosis (arteriolopathy)
- the scale distinguishes two regions of white matter:
- Periventricular White Matter (PVWM)
- Deep White Matter (DWM)
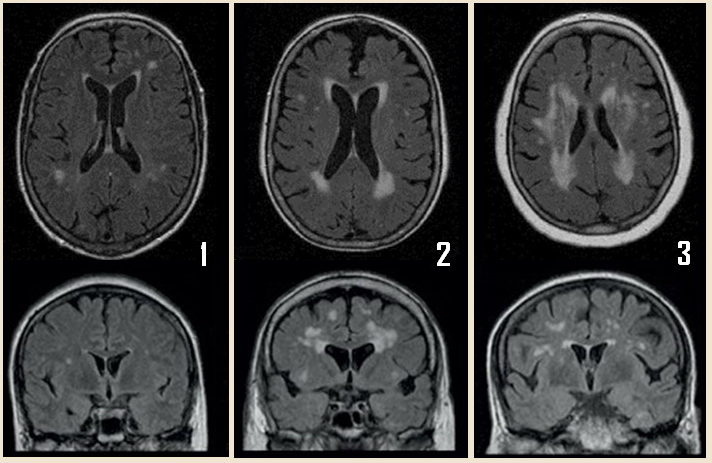
- each region is assessed in terms of the number, size, and confluence of lesions
- optimal assessment is achieved on transverse FLAIR or T2 images
- in routine practice, the scale is often replaced by the terms mild, moderate, and severe to describe the severity of lesions
- periventricular white matter lesions (PVWM) are not exclusively of ischemic origin (may result from demyelination, subependymal gliosis, ependymitis, etc.)
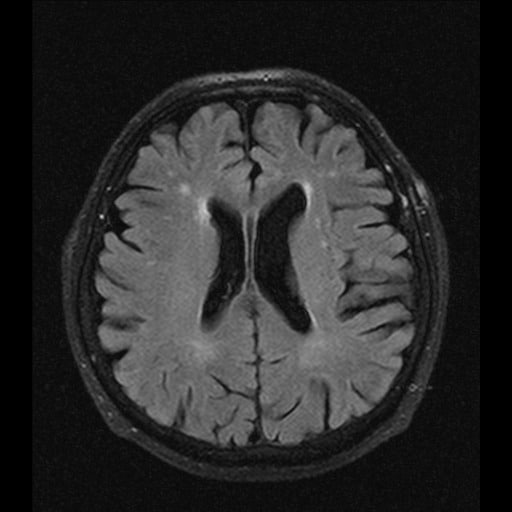
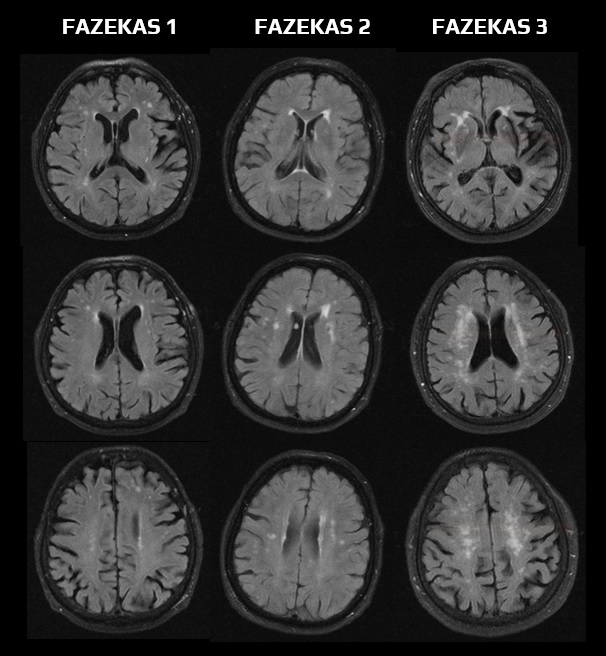
- 0 = no lesion
- 1 = “caps” or pencil-thin lining
- 2 = smooth “halo”
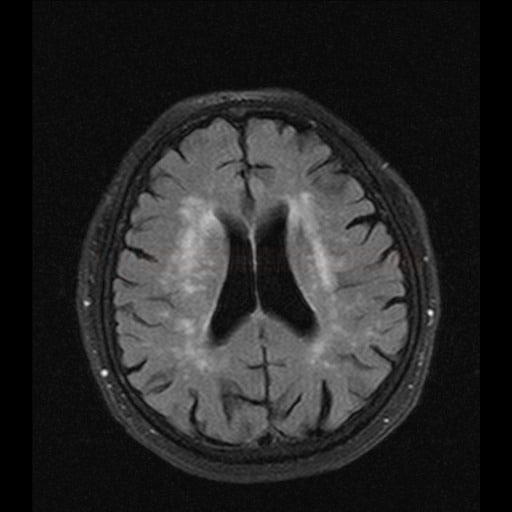
- 3 = irregular periventricular signal extending into the deep white matter
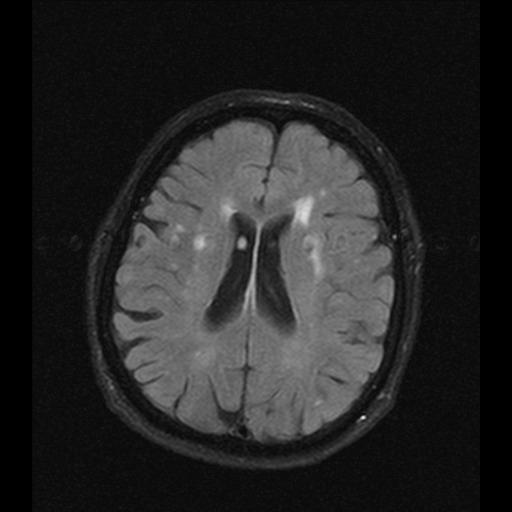
- 0 = no lesion
- therefore, only deep white matter (DWM) should be assessed when monitoring vascular changes (FAZEKAS 0-3)
- 0 = no lesion
- 1 = punctate lesions
- 2 = beginning confluence
- 3 = extensive confluent areas