ISCHEMIC STROKE
Binswanger’s disease
Updated on 08/03/2024, published on 18/02/2022
- Binswanger’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by ischemic damage to the white matter and deep brain structures (basal ganglia and thalamus)
- usually can be seen in individuals over 50 years of age and is caused by small vessel disease and branch artery atherosclerosis
- typically observed in individuals with long-term and poorly controlled hypertension and other vascular risk factors
- clinically characterized by a progressive motor impairment and vascular cognitive deficit (VCI)
- synonyms used in the literature:
- Binswanger’s encephalopathy
- subcortical leukoencephalopathy
- multi-infarct or vascular dementia of the Binswanger type
- subcortical ischemic vascular disease
- subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE)
- small vessel dementia
Etiology
- arteriolopathy, atherosclerosis, thromboembolism
- mostly small penetrating artery disease
- mostly small penetrating artery disease
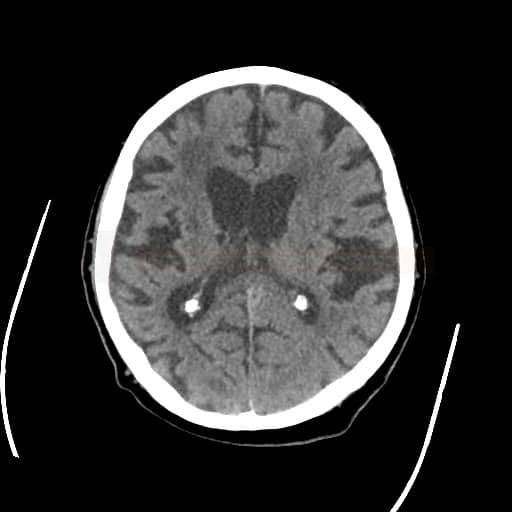
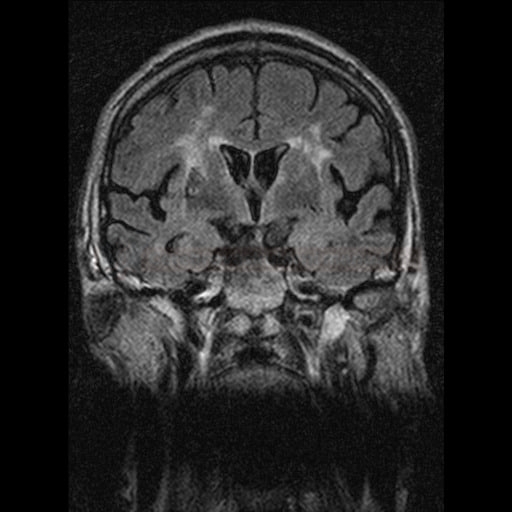
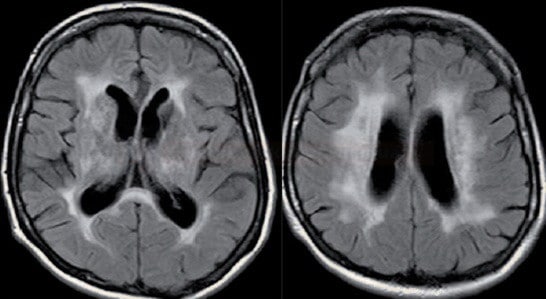
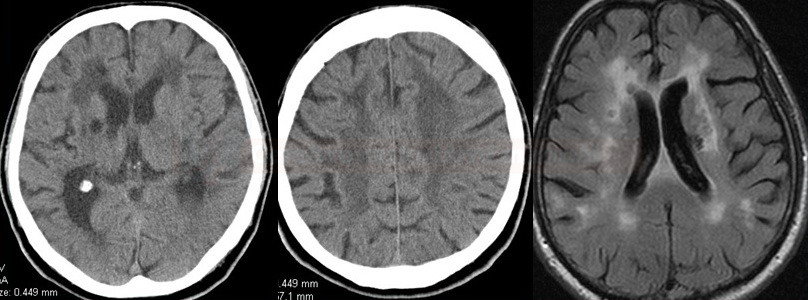
- lesions are relatively symmetrical and diffuse – deep periventricular white matter lesions + lacunar infarcts in basal ganglia, thalamus, and brainstem (pons)
Clinical presentation
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |
Diagnostic evaluation
- typical clinical presentation and imaging findings +vascular risk factors (especially hypertension)
Imaging methods
- CT: symmetrical hypodensities in the deep white matter + lacunar infarcts + brain atrophy
- MRI (FLAIR, T2): extensive periventricular and subcortical white matter lesions + subcortical lacunar infarcts + brain atrophy
Differential diagnosis
- CADASIL (Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy)
- normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
- triad of symptoms: gait disturbance, sphincter insufficiency, and cognitive deterioration (similar to Binswanger’s disease)
- a rather fluent, gradual progression (whereas Binswanger’s disease usually has a stepwise course)
- ventricular dilatation in NPH x convexal atrophy in Binswanger’s disease
- CNS vasculitis
- Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
- Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)
- Frontotemporal dementia (FTD)
Management
Prevention of cerebrovascular disease
- the disease is irreversible; therapy may slow down or halt its progression
- antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy may be considered to reduce the risk of thromboembolic events
- aggressive treatment of arterial hypertension
- aggressive treatment of other vascular risk factors (e.g., diabetes, hyperlipidemia, etc.)
Symptomatic therapy
- symptomatic psychiatric therapy
- antidepressants
- high prevalence of depression in individuals with Binswanger’s disease
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are preferred
- anxiolytic drugs
- choose medications that have minimal sedative effects to avoid exacerbating cognitive impairment
- hypnotic drugs
- antidepressants
- cognitive enhancers – cholinergic deficiency is assumed in VaD (vascular dementia)
- studies have shown some effects of both donepezil and rivastigmine (acetylcholinesterase inhibitors) Black, 2003][Birks, 2013]
- physical and occupational therapy aims to:
- maintain mobility and reduce the risk of falls
- help patients adapt to physical limitations and learn techniques to maintain independence in daily activities for as long as possible