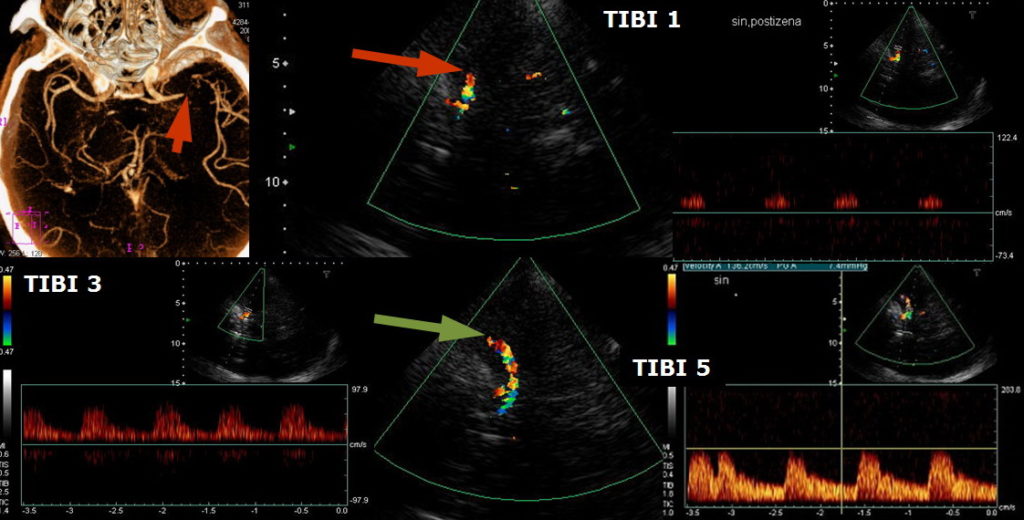
NEUROIMAGING / NEUROSONOLOGY
Thrombolysis in Brain Ischemia (TIBI)
Updated on 20/09/2023, published on 14/02/2023
- the TIBI classification was developed to grade residual flow
- it correlates with initial stroke severity, clinical recovery, and mortality in acute stroke patients
- no improvement in the residual flow correlates with the absence of early clinical recovery and increased mortality (Demchuk, 2012)
- no improvement in the residual flow correlates with the absence of early clinical recovery and increased mortality (Demchuk, 2012)
According to [Demchuk, 2001]
| Recanalization assessment [Clotbust, 2007] |
|
| Complete recanalization | TIBI 4-5 |
| Parcial recanalization | increase of TIBI by ≥1 grade (but not to 4 or 5) |
| Reocclusion | decrease of TIBI by ≤1 grade |