ISCHEMIC STROKE
Carotid artery web
Updated on 14/03/2024, published on 12/01/2023
Definition
- the carotid artery web (CaW) is characterized by a thin fibrous membrane extending from the posterior wall of the carotid bulb into the lumen, just above the bifurcation
- it is considered a variant of fibromuscular dysplasia [Kim, 2019]
- various synonyms are used for this condition: carotid weblike formation, carotid pseudovalvular fold, carotid diaphragm
- a relatively rare vascular pathology, increasingly recognized as an important cause of ischemic stroke in patients without traditional cardiovascular risk factors
- associated with an increased risk of cryptogenic and recurrent ischemic stroke (studies have shown an incidence rate of 8.9% for carotid web in cryptogenic stroke, compared to 1.9% in the control group) [Coutinho, 2017]
- its thrombogenic potential is attributed to blood stasis along the downstream surface of the web, which may increase the risk of intracranial thromboembolism [Compagne, 2019]
Epidemiology
- a relatively rare finding (approximately 1-2.5% of CTAs performed) (Coutinho, 2017) [Compagne, 2017]
- more common in women
Clinical presentation
- often an asymptomatic, incidental lesion
- thrombus formation can lead to recurrent stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- recurrence occurs in up to 29% of patients despite medical treatment [Haussen, 2019]
- carotid artery web is a significant cause of “cryptogenic stroke” in young patients
Diagnostic evaluation
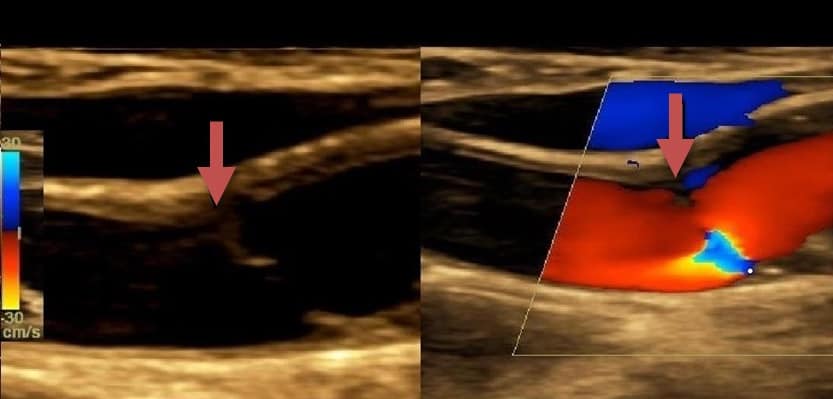
- neurosonology
- an echogenic membrane-like structure protruding into the lumen from the posterior wall at the beginning of the ICA
- concurrent hypoechoic thrombus with possible stenosis may co-occur (Ning, 2020)
- ultrasound is less reliable than CT angiography (CTA) – carotid webs could be easily confused with ulcerations on the surface of the atherosclerosis plaque
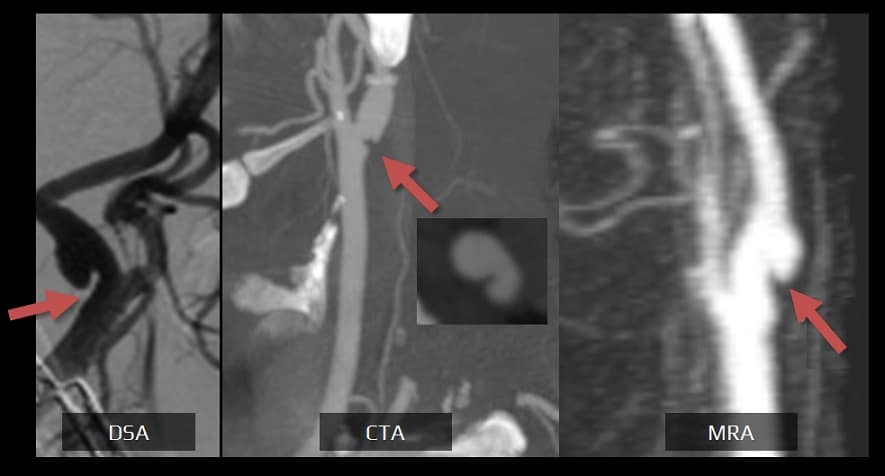
- CTA/MRA
- optimal methods for evaluation
- view both axial and sagittal sections
- the carotid web appears as a thin shelf-like or linear filling defect in the posterior wall of the carotid bulb
- hypodense thrombus is found in up to 25% of cases
- DSA
- considered the gold standard
- carotid web is typically detected during an endovascular procedure
- always look for oblique projections
- signs of contrast stagnation may sometimes be visible in the venous phase
Management
Acute stroke therapy
- recanalization therapy for all eligible patients
- antithrombotic drugs for the rest
Stroke prevention
- there is limited evidence to establish a clear preference between medication and CEA/CAS; some smaller studies report a lower risk of stroke with invasive therapy
- data regarding the management of asymptomatic lesions is insufficient
- medical treatment – current guidelines recommend antiplatelet drugs
- recommended for all stroke (symptomatic) patients (AHA/ASA 2021 1/B-NR)
- antiplatelets may be considered for asymptomatic lesions, although the benefit is not well defined
- indication for anticoagulation is unclear (may be considered in patients with proven concurrent thrombosis); data are limited
- the comparative efficacy of SAPT, DAPT, or anticoagulation is unknown
- CEA/CAS
- medical management alone may not provide adequate protection due to high recurrence risk [Guglielmi, 2021] [Zhang, 2018]
- patients with symptomatic CaW have as high as a 20% risk of stroke recurrence over 2 years (Olindo, 2021)
- invasive therapy should be considered for patients with webs causing significant stenosis and recurrent stroke despite the best medical treatment (BMT) (AHA/ASA 2021 2b/C-LD)
- CaW may be safely and effectively treated with carotid stenting; CEA also allows for histological assessment of CaWs to confirm the diagnosis (Haynes, 2020)
FAQs
- a rare vascular abnormality characterized by an intimal shelf-like protrusion within the carotid artery, typically at the level of the carotid bulb
- this web can disrupt laminar blood flow, predisposing to thrombus formation and subsequent embolic stroke
- its exact prevalence is not well-documented due to its rarity and often asymptomatic nature
- vascular imaging, such as carotid ultrasound, CT or MR angiography, is used to visualize thin, linear, membrane originating from the posterior carotid artery wall and protruding into the vessel lumen
- in the B‐mode, under longitudinal view, the characteristic appearance of CaW is a triangular lesion protruding into the artery lumen
- CAW is often asymptomatic
- rarely, thrombus formation may lead to artery-to-artery embolic event, particularly in young and middle-aged adults without traditional cardiovascular risk factors
- there are no well-defined risk factors for CAW, unlike atherosclerotic disease, which is associated with traditional cardiovascular risk factors
- management strategies include medical and procedural interventions
- medical management is often the first-line treatment and typically involves antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulation
- in selected cases, especially those with recurrent strokes despite optimal medical therapy, endovascular treatment with stenting or surgical intervention such as carotid endarterectomy may be considered
- vascular imaging (usually ultrasound or MRA) can be used to monitor the condition and assess the effectiveness of treatment
- CAW is a structural anomaly related to fibromuscular dysplasia, presenting as an intimal flap or web that predisposes to thrombus formation without a significant stenosis
- atherosclerosis involves the formation of plaques that can narrow the arterial lumen and cause hypoperfusion or embolic events (caused by dislodged atheroma masses or thrombi)
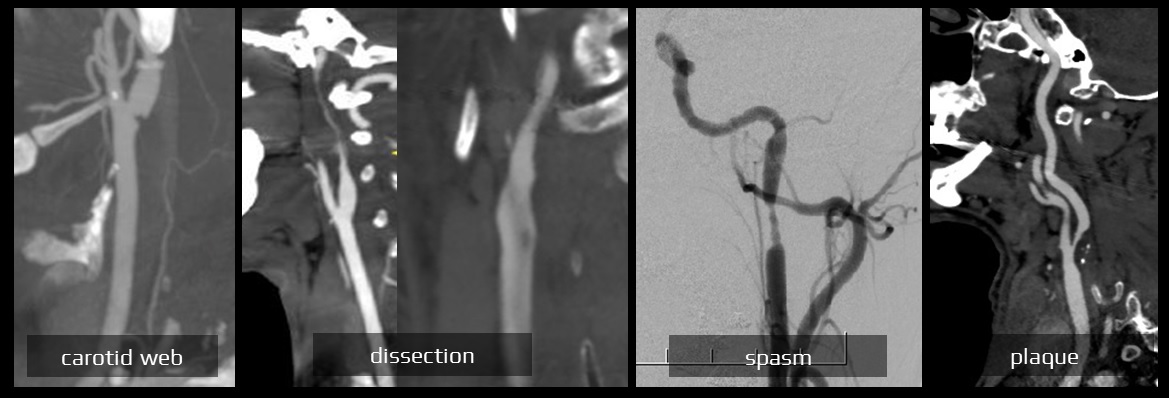
- carotid web can be distinguished from dissection by its characteristic location and appearance, being thin and focal in nature and exclusively located in the posterior wall of the carotid bulb
- more studies are needed for a better understanding carotid web origin; it is considered to be a rare variant of fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)