NEUROIMAGING / NEUROSONOLOGY
TCD/TCCD vasospasm monitoring
Updated on 19/06/2024, published on 31/03/2021
- vasospasm is a contraction of the muscular wall of an artery, resulting in its stenosis and reduced flow
- the prevalence of vasospasms (VSP) following SAH is 50-70%
- vasospasms in SAH patients occur around days 3 to 5 and last up to 3-4 weeks
- approx. 30% of patients with aneurysmal SAH develop delayed ischemic deficit (DID) (Yamaki, 2019)
- DID is the leading preventable cause of poor outcome
- increased risk of VSP is associated with:
- higher Hunt-Hess and Fisher scores
- baseline blood pressure
- fluid depletion
- low ejection fraction (EF)
- the risk of complications increases with the number of affected arteries and hemodynamically significant spasms
Methods for Vasospasms Detection and Monitoring
- transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCCD/TCD)
- optimal bedside, cost-effective, and non-invasive method
- CT angiography
- CT perfusion imaging (CTP) may help predict DID
- MR angiography
- low sensitivity for detection of distal vasospasms
- MR perfusion may help predict DID
- digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
- reserved for local endovascular treatment
- reserved for local endovascular treatment
TCCD criteria
- it is recommended to start the examination on days 2-3 to obtain baseline velocities and then repeat every 24 hours to assess the dynamics
- examine:
- PSV, EDV, Vmean
- PI and RI → more here
- to exclude the effect of hyperemia, determine the ACM/ACI ratio (Lindegaard Ratio – LR)
- a value of LR >3 indicates spasm
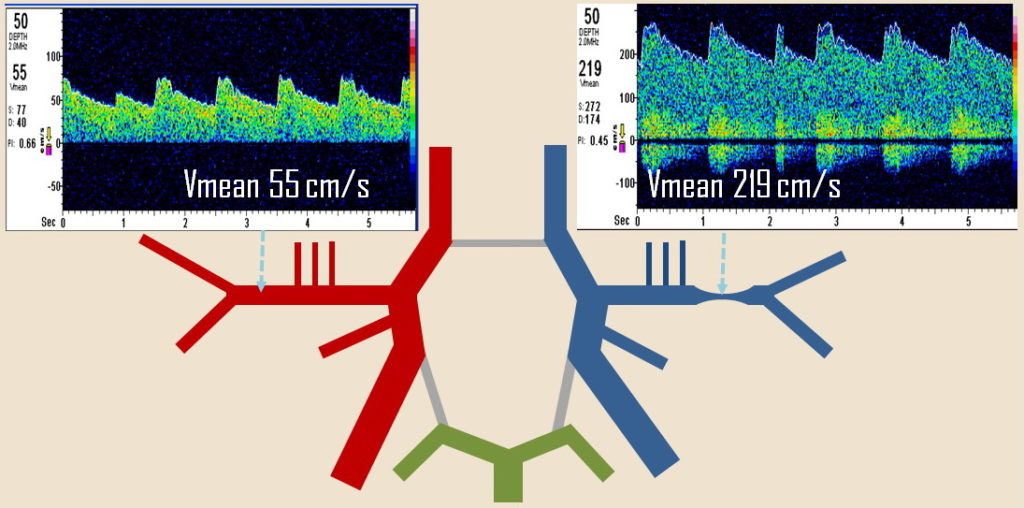
- a significant increase in velocity indicates vasospasm [Vora, 1999] [Lindegaard,1988]
- Vmean ≥ 120 cm/s ( ACM, ACA) + LR >3
- Vmean ≥ 80 cm/s (AV)
- Vmean ≥ 85-95 cm/s (AB) + LR > 2.5-3
- critical value is ↑ Vmean > 50 cm/s/24 h or > 25%/24 h
Vmean = 1/3 (PSV-EDV)+ EDV
- there is no correlation between the severity of vasospasm detected by ultrasound and the clinical course; the development of DID cannot be reliably predicted
- a sudden increase in peripheral resistance (PI > 1.5) indicates either distal VSP or decompensated intracranial hypertension (if detected in multiple vessels)
|
Vessel
|
Vmean
|
Sensitivity/specificity
|
|
MCA, ACA
|
≥ 120 cm/s
≥ 200 cm/s (severe spasm) |
88% / 78%
27% / 98% |
|
ICA
|
≥ 90 cm/s
|
25 % / 93%
|
|
VA
BA |
≥ 60-80 cm/s
≥ 85-95 cm/s |
44% / 79% (60cm/s)
77% / 79% (60 cm/s) |
|
||
| Lindegaard Ratio | vasospasm on DSA |
| < 3 | no VSP |
| 3-4.5 | mild VSP |
| 4.5-6 | moderate VSP |
| > 6 | sever VSP |