NEUROIMAGING
Optic Nerve Sheath ultrasound
Updated on 11/03/2024, published on 25/01/2024
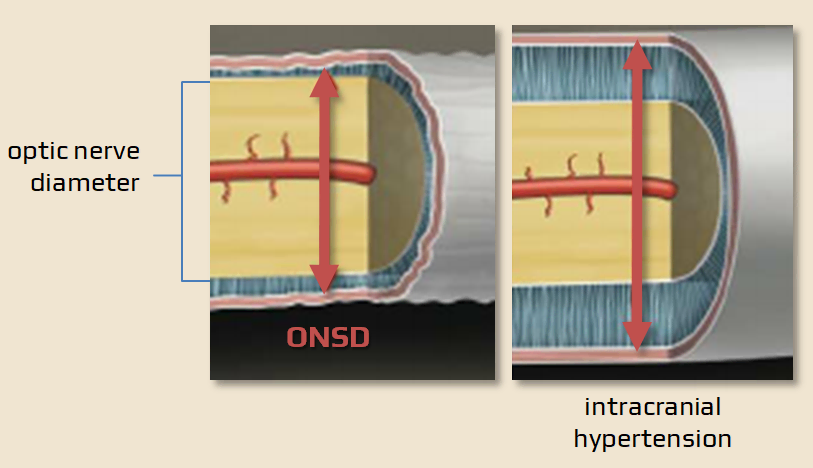
Optic nerve sheath (ONS)
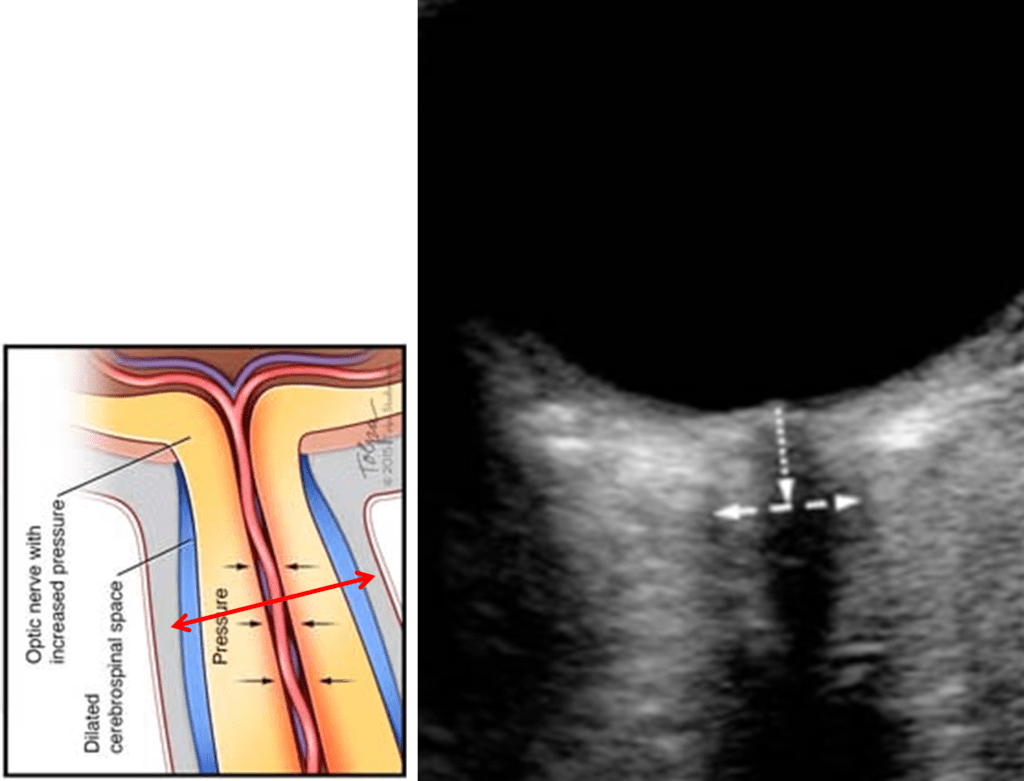
- the optic nerve sheath (ONS) is an anatomical extension of the dura mater, and the subarachnoid space around the optic nerve is continuous with the intracranial subarachnoid space
- any pressure rise within the intracranial compartment impacts the optic nerve head as swelling of the optic disc and papilledema
- however, papilledema evolves and may be a delayed manifestation, besides requiring a skilled observer for precise identification
- dilatation of the optic nerve sheath is a much earlier manifestation of ICP rise
- the optic nerve sheath is fairly easy to visualize by insonation via the orbit
Optic Nerve Sheath UltraSound (ONSUS)
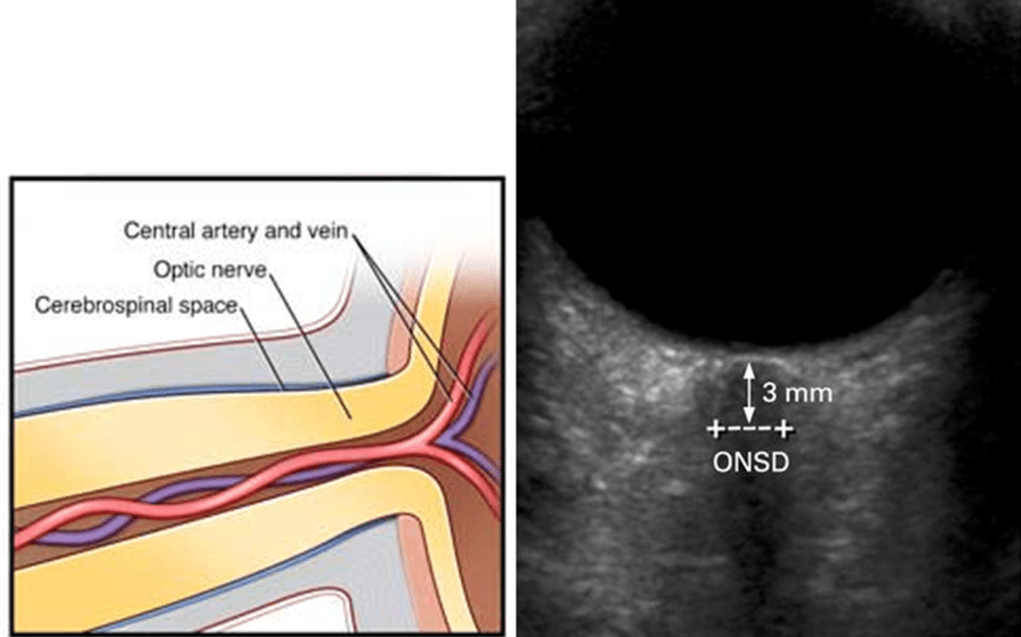
- optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) is evaluated via transorbital window using a 9-12 MHz probe [Dubourgh, 2011]
- measurement provides a dynamic value because ONS responds rapidly to changes in ICP (unlike papilledema)
- it is measured ~ 3 mm posterior to the globe
- normal ONSD: typically 4.0-5.4 mm with an upper limit ranging from 5.0 to 5.7 mm [Chacko, 2014]
- there are considerable differences across studies on the upper cut-off values
- ONSD < 5 mm means normal finding, ONSD > 6 mm is definitely pathological
- a normal ONSD does not exclude serious brain pathology, and the patient still may need further investigation (such as CT, MRI, or lumbar puncture)
- the cut-off value indicating intracranial hypertension > 5.7 mm (various values are reported)
- 6.4 ± 0.6 mm [ Bäuerle, 2012]
- 6.3 ± 0.6 mm on MRI [Geeraerts, 2008]
- cut-off value indicating brain death 7.2 ± 0.4 mm [Lovrencic-Huzjan, 2012]
Pitfalls
- the problem is that a lot of patients fall into the ~5-6 mm grey zone
- additional features may help sort out these patients
Papilledema
- papilledema was traditionally diagnosed with an ophthalmoscope, which is rarely performed in critical care practice
- optic disc elevation may also be detected using ultrasonography using the same view used to determine optic nerve sheath diameter
- optic disc height on ultrasonography correlated well with optical coherence tomography among 14 patients evaluated in an ophthalmology clinic (Teismann, 2013)
- ultrasound thus confirms papilledema (edema due to raised ICP) in 2 ways (disc elevation + increased ONSD)
| normal ONSD | enlarged ONSD | |
| papilledema – | normal | acutely elevated ICP (not enough time to form disk swelling) |
| papilledema + | pseudo-papilledema | ICP elevation |
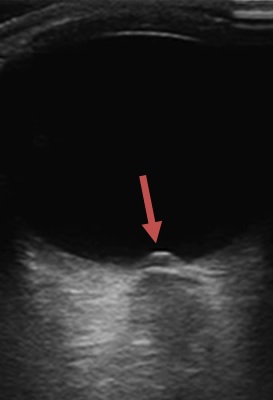
Optic disc drusen
- calcium deposits within the optic disc create a very bright signal with a shadow
- the finding may prove pseudo-papilledema (if ONSD is normal)
Neuritis
- inflammation of the nerve may occur (optic neuritis, sarcoidosis, syphilis, lupus, etc.)
- typically, unilateral optic nerve edema may be observed