ADDONS / ANATOMY
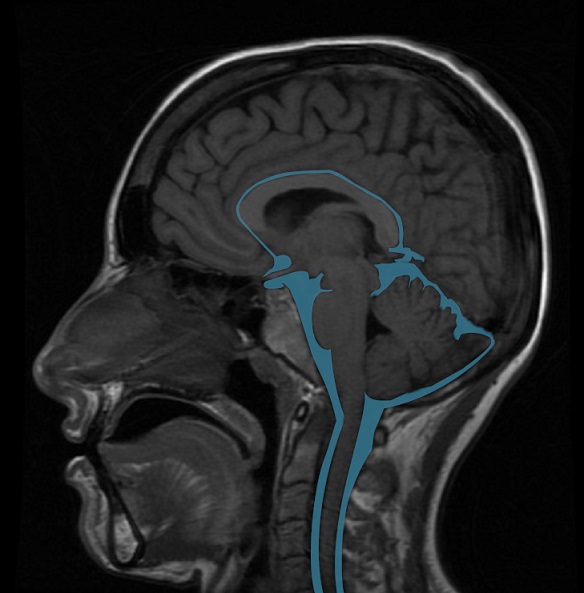
Subarachnoid (basal) cisterns
Updated on 08/03/2024, published on 06/03/2024
The subarachnoid cisterns are compartments in which the pia mater and arachnoid membrane are not in close contact and form cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). They are interconnected, and their patency is essential for the proper circulation of CSF. These cisterns are located at the base of the brain and are therefore also called basal cisterns). Cisterns may have vessels and/or cranial nerves passing through them.
- cisterna magna (unpaired): posterior to the medulla, the largest of the subarachnoid cisterns
- premedullary cistern (unpaired): anterior to the medulla
- cerebellomedullary (lateral cerebellomedullary) cisterns (paired): lateral to the medulla oblongata
- cerebellopontine (cerebellopontine angle) cisterns (paired): lateral to the pons, at the cerebellopontine angle
- prepontine cistern (unpaired): anterior to the pons
- superior cerebellar cistern (unpaired): posterior to the quadrigeminal cistern, between the superior surface of cerebellum and tentorium
- perimesencephalic cisterns
- interpeduncular cistern (unpaired): between the cerebral crura
- crural cisterns (paired): between the cerebral crus and uncus of the temporal lobe
- ambient cisterns (paired): posterolateral to the midbrain
- quadrigeminal cistern (unpaired): between colliculi, splenium of the corpus callosum, and superior surface of the cerebellum
- suprasellar (chiasmatic) cistern (unpaired): anterior to the interpeduncular cistern, surrounding the infundibulum and optic chiasm
- carotid cistern (paired): lateral to the suprasellar cistern, surrounds the supraclinoid internal carotid artery
- cistern of the lamina terminalis (unpaired): superior to the suprasellar cistern, anterior to the anterior wall of the third ventricle
- Sylvian cistern (paired): deep part of the Sylvian fissure
- cistern of the velum interpositum (unpaired): between the layers of tela choroidea in the roof of the third ventricle
- pericallosal cistern (unpaired): superior to the cistern of the lamina terminalis, superior to the corpus callosum