ADDONS / SCALES
ASPECTS
Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score
Updated on 25/12/2023, published on 22/03/2021
- the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) is used to standardize and increase the reliability of detecting early signs of ischemia
- early ischemic changes are defined as incipient parenchymal hypodensity or loss of grey and white matter differentiation
- ASPECTS can be assessed on:
- noncontrast CT (NCCT) – adjust width/level
- CT perfusion (CTP) [Aviv, 2007]
- CTA source images (CTA-SI) [Puetz, 2009]
- noncontrast CT (NCCT) – adjust width/level
- ASPECTS primarily evaluates the MCA territory
- PC-ASPECTS was designed to evaluate changes in the posterior circulation
- commercial software programs for automated ASPECTS evaluation are available (e.g., BRAINOMIX)
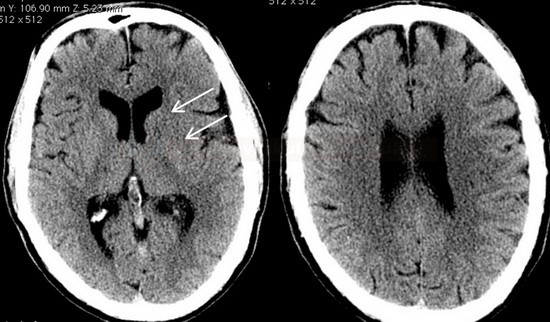
MCA territory
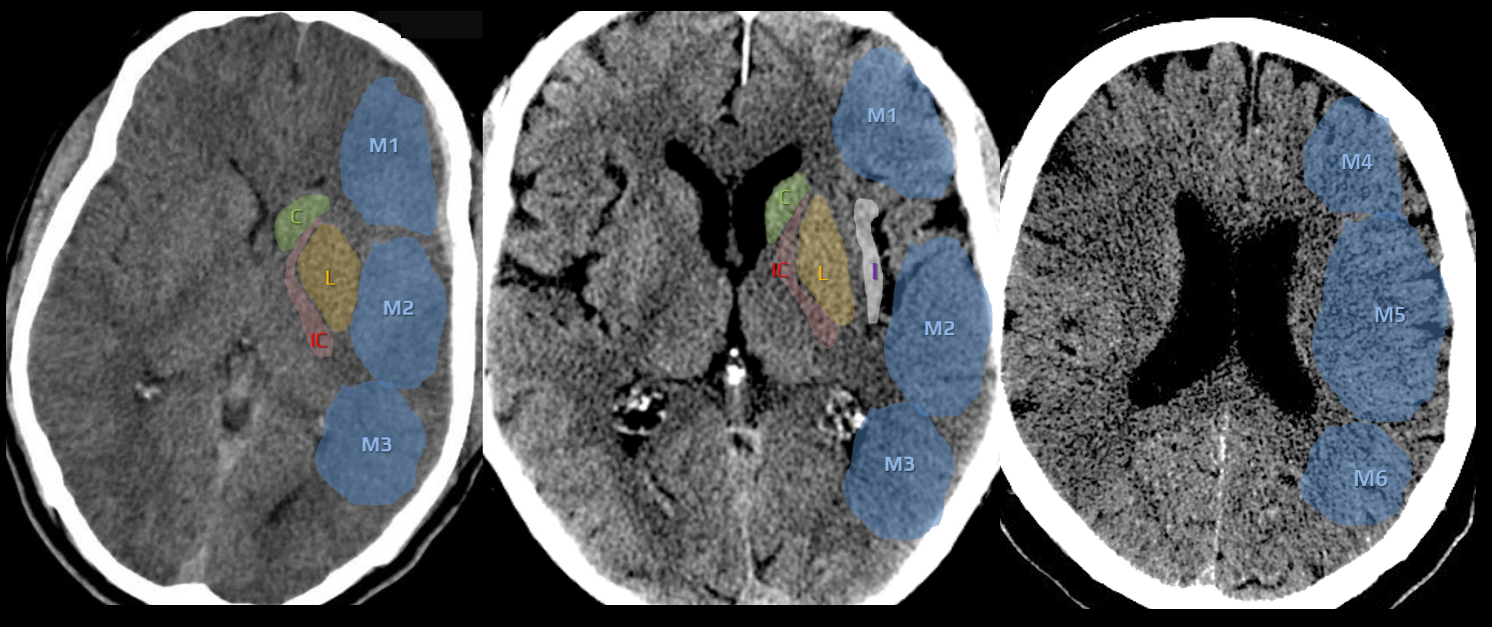
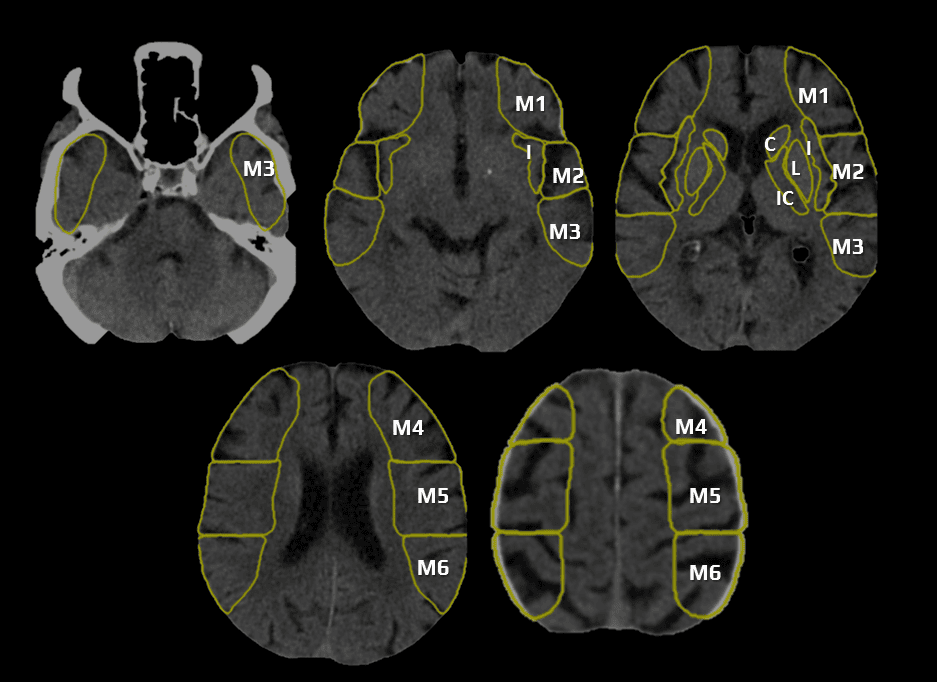
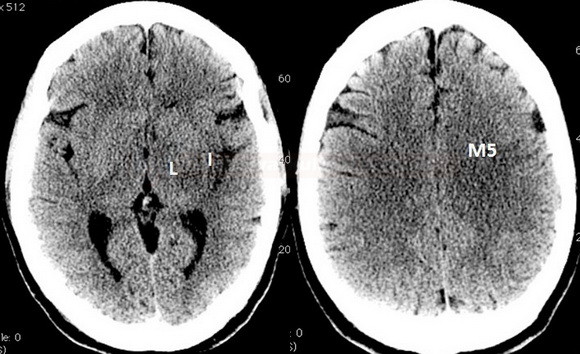
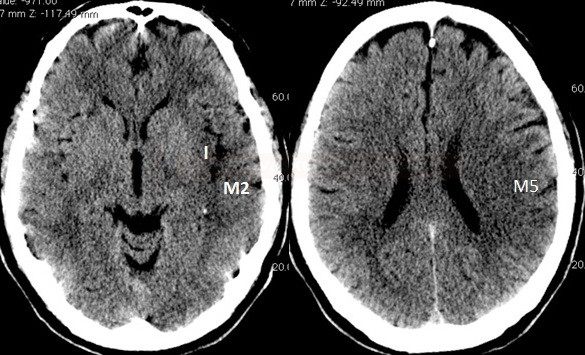
- a 10-point quantitative CT scan score used for evaluating patients with stroke in the MCA territory
- a score of 10 points indicates a normal finding; 1 point is subtracted from the initial score of 10 for each region exhibiting early signs of ischemia
- C – caudate nucleus
- L – lentiform nucleus
- IC – internal capsule (any portion)
- I – insular cortex
- C, L, IC, I, and M1-3 are assessed on axial scans at the basal ganglia level
- M1 – anterior MCA cortex, corresponding to the frontal operculum
- M2 – MCA cortex lateral to the insular ribbon, corresponding to the anterior temporal lobe
- M3 – posterior MCA cortex corresponding to the posterior temporal lobe
- M4-5 are above the basal ganglia at the level of the lateral ventricles (supraganglionic level)
- M4 – anterior MCA territory immediately superior to M1
- M5 – lateral MCA territory immediately superior to M2
- M6 – posterior MCA territory immediately superior to M3
- ASPECTS is a valuable technique for prognostic evaluation in acute ischemic stroke (thresholds may vary slightly between NCCT and CTP)
- patients with high ASPECTS values are more likely to have favorable outcomes
- an NCCT ASPECTS score of ≤ 7 predicts worse functional outcome at three months [Esmael, 2021]
- patients with CTP ASPECTS score of < 8 treated with thrombolysis mainly did not achieve favorable clinical outcomes [Aviv, 2007]
- the threshold for thrombectomy is gradually decreasing (probably ASPECTS 3 based on SELECT2, ANGEL ASPECT trials results) ⇒ ASPECT score will lose some of its importance because most of the patients will be treated anyway
Posterior circulation
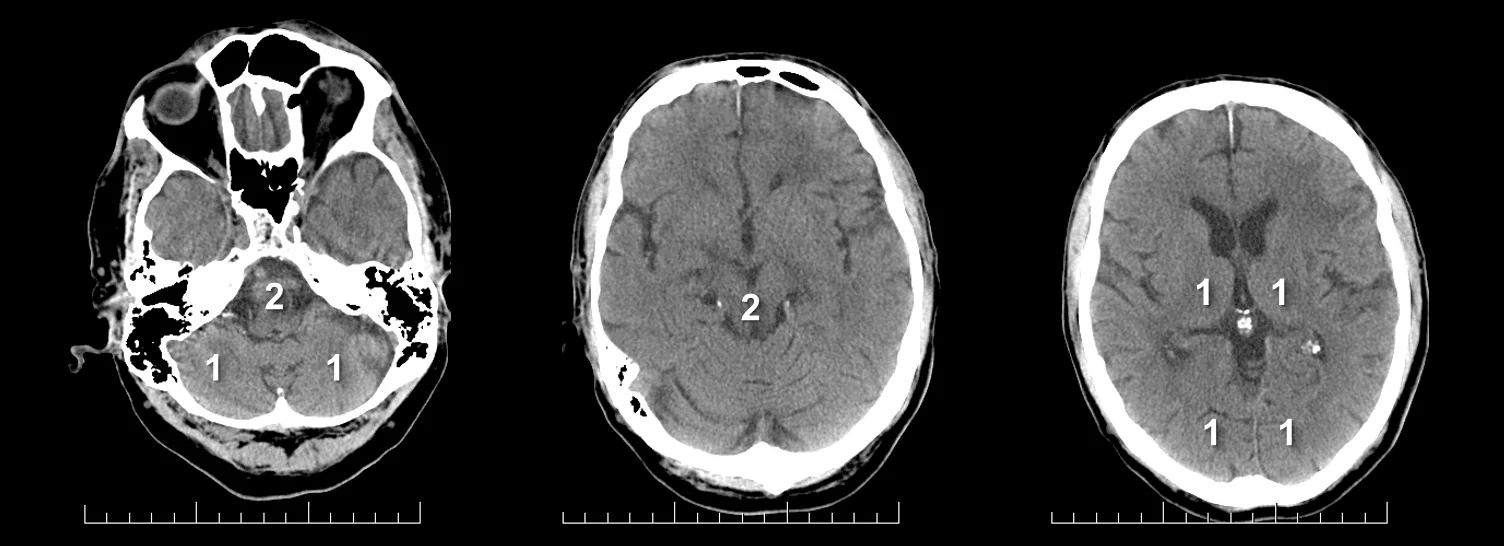
PC-ASPECTS (The posterior circulation Acute Stroke Prognosis Early CT score)
- helps to assess early ischemic changes on noncontrast (NCCT) and optionally on CTA source images (CTA-SI)
- normal brain scores 10; points are subtracted for each affected region:
- thalami (1 point each)
- occipital lobes (1 point each)
- midbrain (2 points – uni- and bilateral)
- pons (2 points – uni- and bilateral)
- cerebellar hemispheres (1 point each)
- pc-ASPECTS < 8 is associated with poor prognosis [Puetz, 2009]
- assessing can be inaccurate in the following situations:
- recent ischemia superimposed on an older lesion
- extensive leukoencephalopathy
- poor image quality

![pc-aspects_prognosis - Puetz pc-ASPECT score predicts prognosis [Puetz, 2009]](https://www.stroke-manual.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/pc-aspects_prognosis-Puetz.jpg)


