ADD-ONS / OTHER VASCULAR DISORDERS
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)
Updated on 05/11/2023, published on 15/02/2022
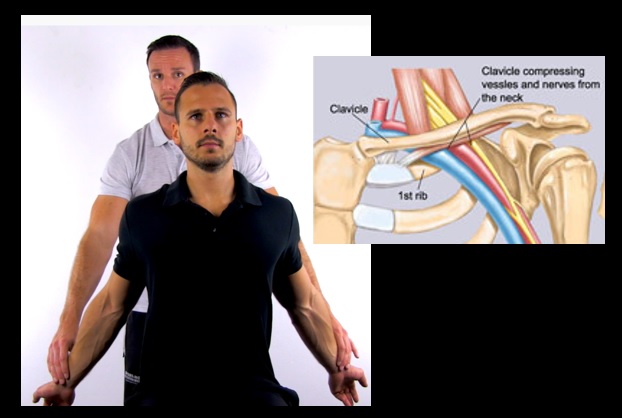
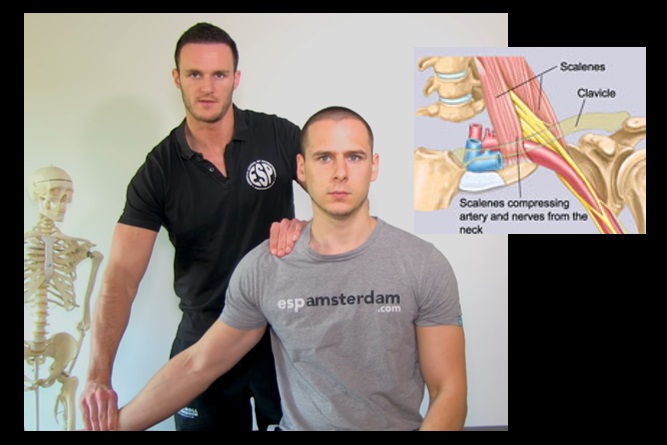
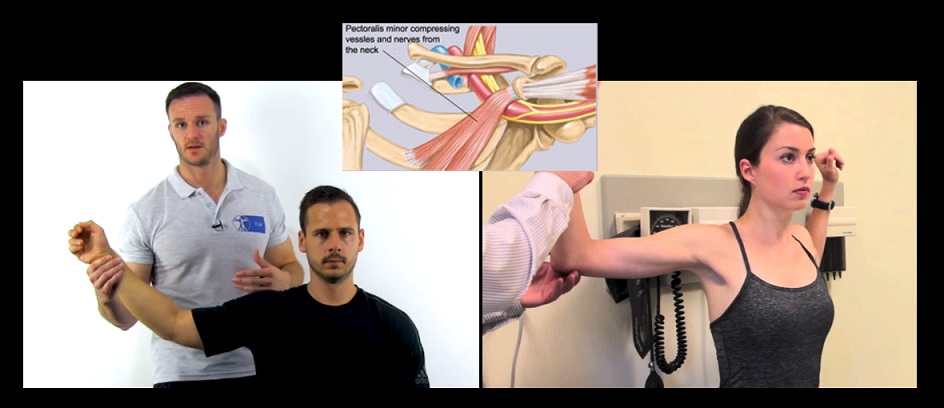
The anatomic condition of the upper thoracic aperture, with or without additional external factors, predisposes to chronic pressure damage to the brachial plexus and vascular compression. This is particularly true for its caudal portion. Since the exact pathogenetic mechanisms cannot always be proven, the general term thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is used.
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |
Classification of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
| Classification according to clinical presentation: | ||||
|
| Etiopathogenetic classification |
||||
|
Etiology
- anatomic anomalies
- cervical rib ( an extra rib that forms above the first rib, growing from the base of the neck just above the collarbone)
- ligamentous band between the spine and rib
- poor posture
- drooping shoulders with anteflexion of the head
- trauma
- difficulties may occur with a delay
- repetitive, monotonous work
- working at the computer, working on a production line, working with prolonged hand-holding
- sports (e.g., swimming)
- repetitive carrying of loads over the shoulder
- pregnancy
- TOS may occur during pregnancy due to joints loosening
Clinical presentation
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |
Diagnostic evaluation
Medical history, clinical examination, provoking tests
Other diagnostic methods
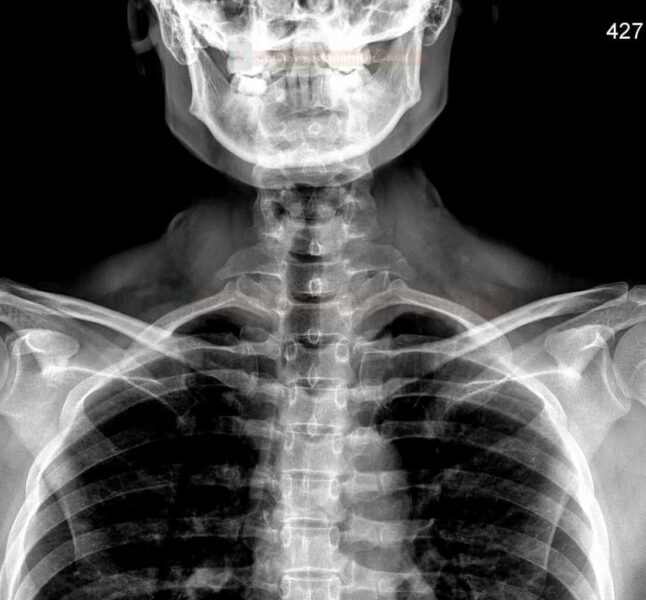
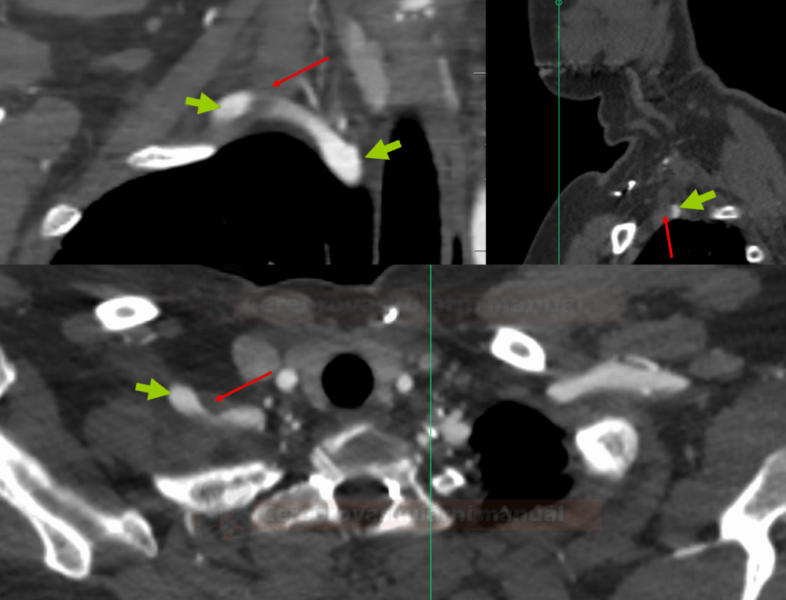
- X-ray of the upper thoracic outlet
- look for cervical rib
- exclude other structural pathologies
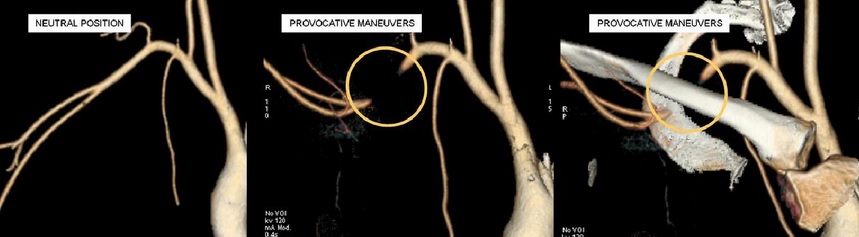
- dynamic DSA/CTA or the Doppler ultrasound (during provocation testing)
- direct demonstration of arterial compression and determination of its severity
- detection of poststenotic dilatation, detection of intraluminal thrombus within the dilated segment
- flow pattern change during the provoking maneuver (ultrasound)
- dampened flow in distal segments + high-resistance flow is found in the proximal subclavian artery
- MRI
- can help locate the site of the plexus or subclavian artery compression
- it can detect a fibrous band between the spine and the 1st rib or cervical rib
- EMG
- detects neuropathic changes
Management
Conservative treatment
- physiotherapy to strengthen the corset and shoulder muscles and improve posture → see here
- relaxation techniques
- medication (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAID)
Surgical treatment
- indications:
- failure of conservative pain management
- progressive neurological symptoms (atrophy, sensory deficit, paresis)
- symptomatic subclavian artery compression with distal hypoperfusion, aneurysm formation, etc.
- surgery provides pain relief and may halt the progression of neurological disability
- there is always a risk of periprocedural brachial plexus injury
- approaches:
- anterior supraclavicular – resection of the cervical rib and potential fibrous band arising from it
- transaxillary – partial resection of the first rib