ADD-ONS / SCALES
Intracerebral hemorrhage scales and scores
Created 26.05.2020, last update 08.06.2022
ICH score
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |
Max-ICH score
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |
Spot sign
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |
HAS-BLED
- a tool to guide the decision to initiate anticoagulation in patients with Afib
- always compare the risk for major bleeding (calculated by the HAS-BLED score) with the risk of thromboembolic events (calculated by the CHA2DS2-VASc score) ⇒ does the benefit of anticoagulation outweigh the risk of bleeding?
- a study comparing HEMORR2HAGES, ATRIA, and HAS-BLED showed superior performance of the HAS-BLED score compared to the other two scores
| HAS-BLED score | ||
| Hypertension |
uncontrolled BP (SBP >160 mmHg)
|
1 |
| Abnormal liver/renal function |
renal disease – dialysis, transplant, Cr >2.26 mg/dL or >200 µmol/L
liver disease – cirrhosis or bilirubin >2x normal or AST/ALT/AP >3x normal |
1 1 |
| Stroke | previous stroke |
1 |
| Bleeding |
prior major bleeding or predisposition to bleeding
|
1 |
| Labile INR | unstable INR, time in therapeutic range <60% | 1 |
| Elderly | age ≥ 65 years |
1 |
| Drugs/alcohol |
medication predisposing to bleeding – aspirin, clopidogrel, NSAIDs
heavy alcohol use |
1 1 |
|
HAS-BLED score
|
Pisters et al. annual ICH risk
|
Lip et al. annual ICH risk
|
| 0 | 1.1% | 0.9% |
| 1 | 1% | 3.4% |
| 2 | 1.9% | 4.1% |
| 3 | 3.7% | 5.8% |
| 4 | 8.7% | 8.9% |
| 5 | 12.5% | 9.1 % |
| Not enough data for higher scores; risk is most likely > 10% |
||
A score ≥ 3 is associated with an increased risk of major bleeding.
Frequent monitoring, DOAC use, or alternatives to anticoagulation (such as LAA occlusion) are recommended.
SMASH-U
| Etiologic Classification of Intracerebral Hemorrhage – SMASH-U [Meretoja, 2012] | ||
| incidence | mortality at 3 months |
|
| Structural lesions (cavernous malformation, AVM) | 5% | 4 % |
| Medication (warfarin, DOAC, antiplatelet therapy) | 14% | 54 % |
| Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy (CAA) |
20% | 22 % |
| Systemic disease (liver, kidney disease, thrombocytopenia/thrombocytopathies) | 5% | 44 % |
| Hypertension | 35% | 33 % |
| Undetermined | 21% | 30% |
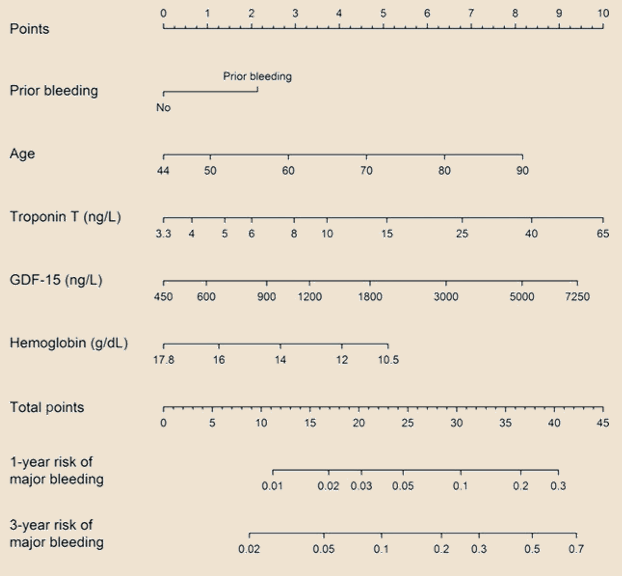
ABC
- in addition to clinical factors, the ABC-bleeding risk score also incorporates the biomarkers: high-sensitivity troponin T, growth differentiation factor–15, and hemoglobin
ORBIT
- The ORBIT bleeding risk score has a superior predictive ability for major bleeding in AFib patients compared to the HAS-BLED and ATRIA risk scores. The ORBIT risk score may provide a simple, easy-to-remember tool to assist in clinical decision-making [O´Brian, 2015] [Hilkens, 2017]
| Older age ( >75 y) | 1 |
| Reduced hemoglobin/Hct/anemia (men <13 g/dL and Hct < 40%, women < 12 g/dL and Hct < 36% ) | 2 |
| Bleeding | 2 |
| Insufficient kidney function (GFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 1 |
| Treatment with antiplatelets | 1 |
| Maximum score | 7 |
|
score 0–2 – low risk ~ 2.4% / y
score 3 – medium risk ~ 4.7% / y
score ≥ 4 – high risk ~ 8.1% / y
|
Spetzler-Martin
- The Spetzler-Martin arteriovenous malformation (AVM) grading system assigns points for various angiographic features to predict the risk of surgery
|
Spetzler-Martin AVM grading scale (grade I-V)
|
||
|
score
|
||
|
Nidus size – largest nidus diameter on angiography
|
1
2
3
|
|
|
The eloquence of the adjacent brain
|
0
1 |
|
|
Venous drainage → Anatomy of veins and sinuses
|
0
1
|
|
HEMORR2HAGES
- the HEMORR2HAGES score is used to stratify patients’ risk of bleeding when using anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation (Afib) in conjunction with situation-specific risks
- a systemic review comparing the performance of HAS-BLED, ATRIA, and HEMORR2HAGES recommended HAS-BLED for assessing major bleeding risk in Afib patients
- HEMORR2HAGES showed higher diagnostic accuracy but was considered more difficult to use due to its complexity
| Hepatic/renal disease |
1 |
| Ethanol abuse |
1 |
| Malignancy history |
1 |
| Older (age >75 y) | 1 |
| Reduced platelet count or function, including aspirin therapy | 1 |
| Re-bleeding risk (history of prior bleeding) | 2 |
| Hypertension (uncontrolled) |
1 |
| Anemia (Hgb <13 g/dL for Men; Hgb <12 g/dL for Women) |
1 |
| Genetic factors (CYP 2C9 single-nucleotide polymorphisms) |
1 |
| Excessive fall risk | 1 |
| Stroke history |
1 |
| Total points | 12 |
|
The annual risk of bleeding
|
|
Score 0 ~ 1.9 %/y
Score 1 ~ 2.5 %/y
Score 2 ~ 5.3 %/y
Score 3 ~ 8.4 %/y
Score 4 ~ 10.4 %/y
Score ≥ 5 ~ 12.3 %/y
|