NEUROIMAGING / DSA
Balloon Test Occlusion (BTO)
Updated on 19/07/2024, published on 29/04/2021
- acute internal carotid artery (ICA) occlusion is associated with a high risk of ischemic neurological deficits (20-49%) (Seet, 2012)
- in a meta-analysis of 20 studies of patients with ICA occlusion, the annual risk of stroke was 5.5% (2.1% ipsilateral). Those with hemodynamic compromise on functional imaging had a stroke risk of 12.5% (9.5% ipsilateral)
- the clinical course of ICA occlusion is variable, ranging from asymptomatic lesions to devastating strokes (Klijn, 1997)
- a balloon test occlusion (BTO) is performed to determine whether an artery can be temporarily or permanently intentionally occluded without significantly affecting brain perfusion
- if the BTO is well tolerated, the risk of subsequent ischemia is significantly reduced, and procedure may be performed
- pharmacologically induced hypotension during BTO further increases the sensitivity of the test
- BTO results can be predicted by angiographic findings (CTA, MRA); a small ipsilateral PCOmA, and more significantly, a small AComA (<1.1 mm) can be used to identify patients who are likely to fail BTO (Mendez, 2022)
Indications
- functional testing in patients scheduled for ICA occlusion (inoperable aneurysms, glomus tumors, intracranial tumors, tumors in the ENT region)
- the Matas test (external CCA compression during angiography) used to be performed; it has been replaced by the more sensitive balloon test occlusion (BTO)
Procedure
Patient preparation
- administer allergy premedication (if necessary)
- nimodipine 60mg (2 tbl.) every 4 hours can be administered for 24 hours before the procedure to prevent vasospasms
- insert a urinary catheter and intravenous cannula
- start normal saline solution at 150 mL/h at least 4h before the procedure
- ensure the presence of an anesthesiologist for supervision
- heparinization during the procedure:
- an initial bolus of HEPARIN 5000 IU IV
- then mix 4mL of Heparin (1ml = 5000jj) + 16mL of NS (20mL solution = 20 000jj) and administer 1-3 mL/h ((1000-3000 IU/h) by IV infusion
- alternatively, additional boluses can be used (1000 to 3000 IU every hour intravenously)
- the target APTT is ~ 2-3x of baseline
- an initial bolus of HEPARIN 5000 IU IV
- flush the distal catheter section above the balloon with normal saline + a low dose of heparin
- 0,5 mL of HEPARIN (500IU) + 500 mL of NS (1mL of solution = 1IU) – via continuous IA infusion 60mL/h (1 IU/min) [Standard, 1995]
Clinical and TCCD monitoring during the procedure
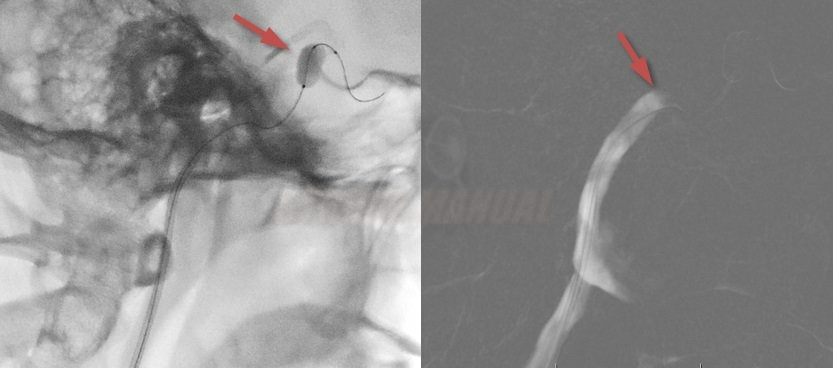
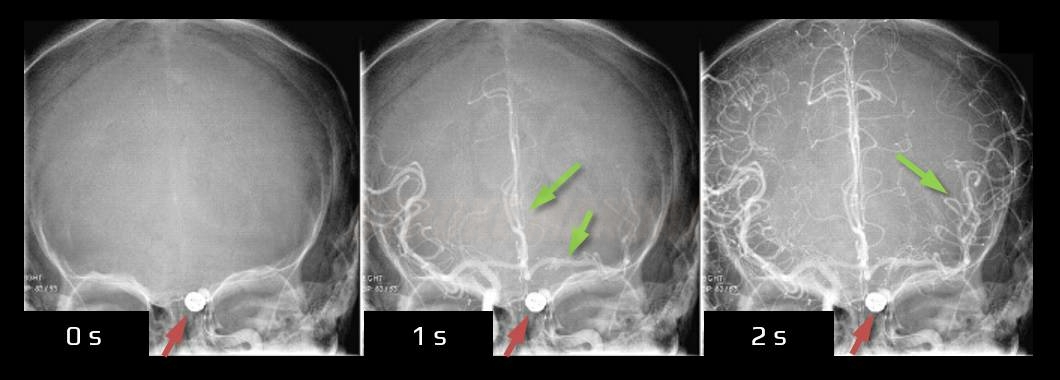
- the balloon is inflated under fluoroscopic observation, and occlusion is confirmed by a control angiogram
- check the neurological status continuously after balloon inflation (continuous verbal dialogue, repeated evaluation of the patient’s muscle strength)
- stop the test:
- if neurological deficits develop (BTO if positive)
- if the patient tolerates occlusion for 20 minutes without neurologic deficits (BTO is negative) [Kikuchi, 2014
- in addition to a neurological examination, TCCD/TCD monitoring of the MCA may be used [Sorteberg,2008]
- if PSV drops to the max. 65% of baseline, ICA occlusion is safe
- if PSV drops to < 54%, there is an increased risk of hypoperfusion
- a 20-minute test with medically induced hypotension may be added
- labetalol IV (bolus 5-20 mg) or sodium nitroprusside (2.5 to 7.5mg/kg/min) are used to lower the mean blood pressure (MAP) to 2/3 of the baseline
- maintain hypotension for ~ 10-20 minutes
- the negative test identifies patients who can safely undergo ICA occlusion with 95% accuracy [Standard, 1995]
- extract the balloon after the test is completed
- neutralize heparin with PROTAMIN → Neutralization of the anticoagulant drugs
- remove the sheath, apply external groin compression or seal the puncture
- observe the patient in the ICU for the next 24 hours
Assessment of collateral circulation
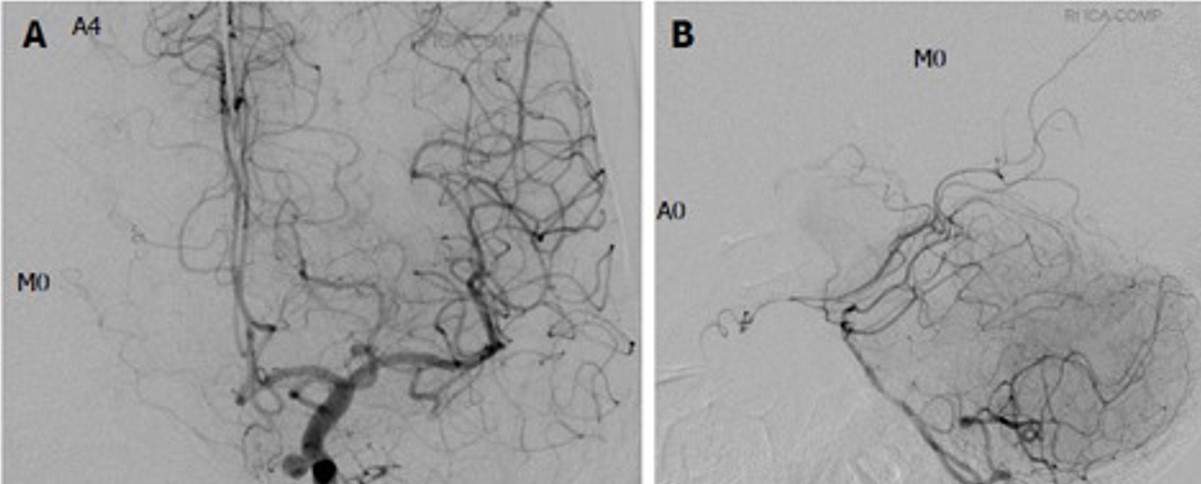
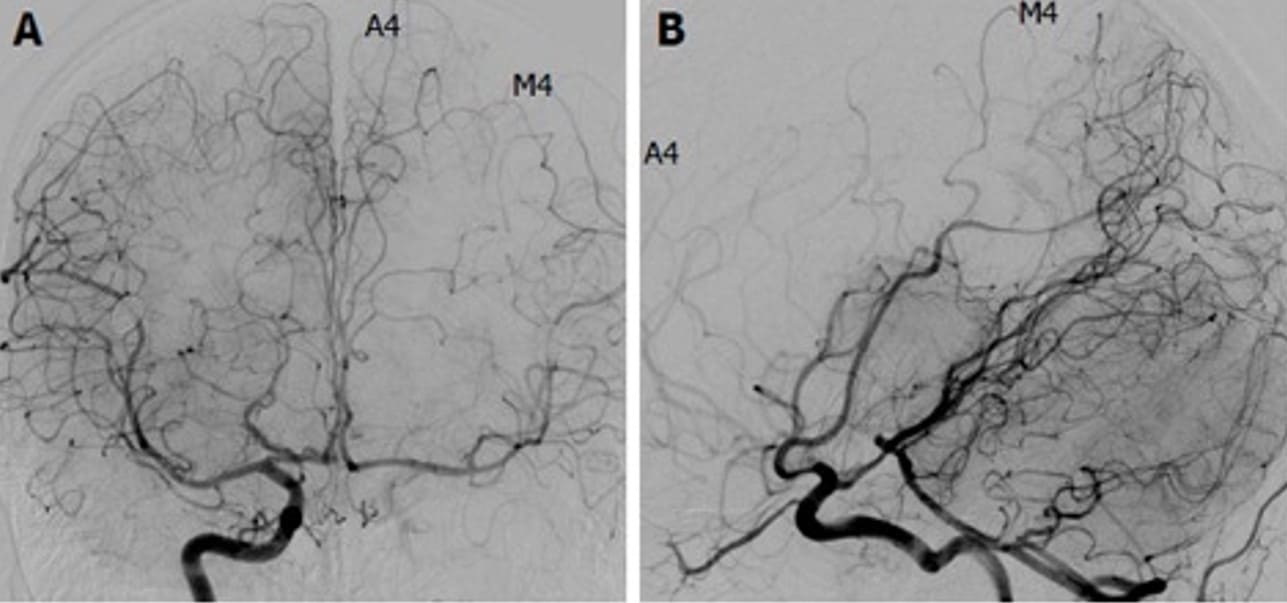
- assess the contrast filling of ACA (A1-A4 segments) and the MCA (segments M1-M4) on the occluded side (Kikuchi, 2014]
- assess the anatomy of the circle of Willis (especially the presence and quality of AComA and PComA, A1 and P1 segments bilaterally)
Complications
- neurologic complications (due to thrombosis or dissection) : 0-8.3% (average complication rate according to various studies ~ 2.2%) → more here