OTHER VASCULAR DISORDERS
Carotid artery risk score
Updated on 03/11/2023, published on 30/05/2023
- Carotid Artery Risk (CAR) score estimates the 5-year ipsilateral stroke rate in recently symptomatic patients with carotid stenosis of ≥ 50% treated with optimized medical therapy (OMT)
- the algorithm incorporates the effects of modern medical management
- the calculator was used to determine patient eligibility for the ECST-2 trial
- ECST-2 trial evaluated the optimal treatment for patients with symptomatic or asymptomatic moderate-to-severe carotid stenosis, who are at low-to-intermediate risk of recurrent stroke
- the trial compared the risks and benefits of OMT alone versus OMT + immediate carotid surgery (or stenting)
- patients with symptomatic stenosis or stenosis that has not caused symptoms for ≥ 180 days were automatically eligible for the ECST-2 trial
- the score serves as a guide; it should not substitute for the judgment of experienced clinicians, who must consider all relevant information about the individual patient
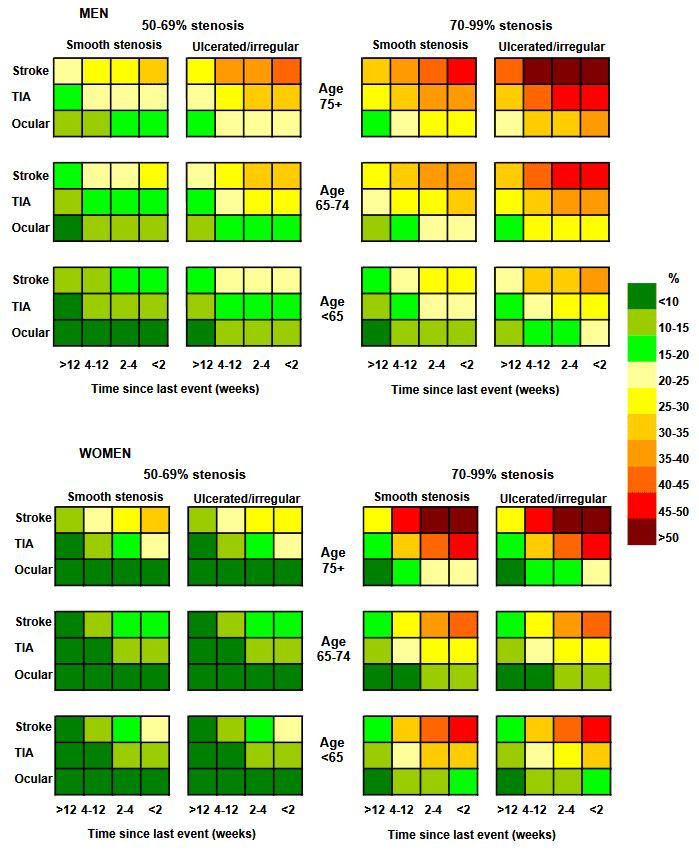
- the color-coded risk tables serve as an alternative to the computer model
- these tables predict the 5-year risk of ipsilateral ischemic stroke in patients with recently symptomatic carotid stenosis who are on medical treatment based on data derived from the ECST model (Rothwell, 1999)
- nearly 430 patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic atherosclerotic carotid stenosis of ≥50% and a Carotid Artery Risk (CAR) score <20% were randomized to optimized medical therapy (OMT) alone or OMT plus revascularization via carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS)
- preliminary results suggest that adding carotid revascularization to OMT does not appear to offer clinical benefit in patients with significant carotid stenosis who have a low-to-intermediate 5-year risk of stroke
- no significant difference exists between the treatment groups at 2 years regarding the rate of a composite endpoint, as well as the occurrence of any stroke, myocardial infarction, and periprocedural death
Explanation of items in the CAR score
- degree of stenosis
- measured by NASCET criteria (50-99%; no evidence of benefit in patients with <50% stenosis)
- if reported by ultrasound as a range of values, use the middle of the range (e.g., for a report saying stenosis 50-59%, enter 55)
- near occlusion – severe (subtotal) stenosis associated with the collapse of the carotid artery distal to the stenosis (string sign)
- time in days since the last event
- risk predictions will not correctly assess the patients who have experienced multiple recurrent events in recent months
- risk predictions will not correctly assess the patients who have experienced multiple recurrent events in recent months
- definition of events
- major stroke = a non-disabling stroke with residual signs present or expected to persist > 7 days
- minor stroke = a stroke with signs and symptoms lasting or expected to last between 24 hours and 7 days
- TIA = symptoms lasting < 24 hours (old definiton)
- multiple TIAs
- monocular symptoms = amaurosis fugax (TIA) or retinal infarction (CRAO)
- plaque ulceration
- clear evidence of ulcerated plaque on noninvasive imaging
- irregular and ulcerated plaques have been shown to correlate highly with with lipid-rich, unstable, or ruptured plaques on histology ⇒ patients with evidence of lipid-rich or unstable/ruptured plaque on noninvasive imaging could, therefore, be recorded as having irregular or ulcerated plaque
- MI – history of myocardial infarction
- PVD – history of peripheral vascular disease (also known as PAD)