NEUROIMAGING
Complications of endovascular procedures
Updated on 04/09/2024, published on 14/04/2023
- endovascular procedures are a cornerstone in the minimally invasive treatment of vascular disorders, encompassing a broad spectrum of interventions from diagnostic angiography to therapeutic endovascular aneurysm repair, stent placement, or thrombectomy
- while these techniques offer significant benefits, they are not without risk
- diagnostic digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is generally associated with a low risk of complications (risk of neurological deficit ~ 0.09-0.14%)
- the risk increases in elderly patients with atherosclerotic disease of aorta and carotid arteries
- most of the complications of endovascular procedures listed below are related to interventional procedures, both acute and elective
Central complications
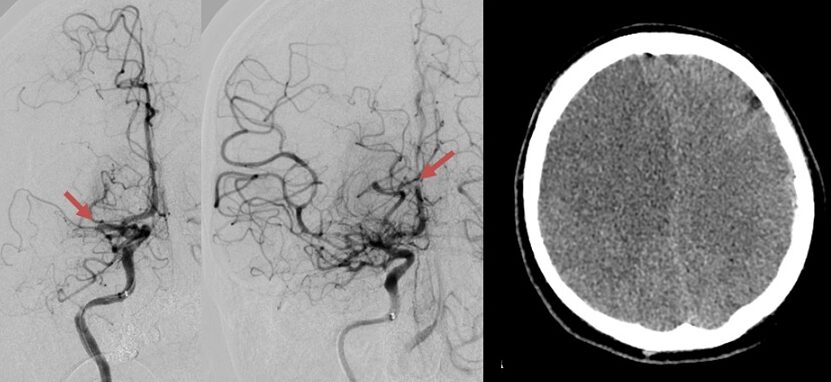
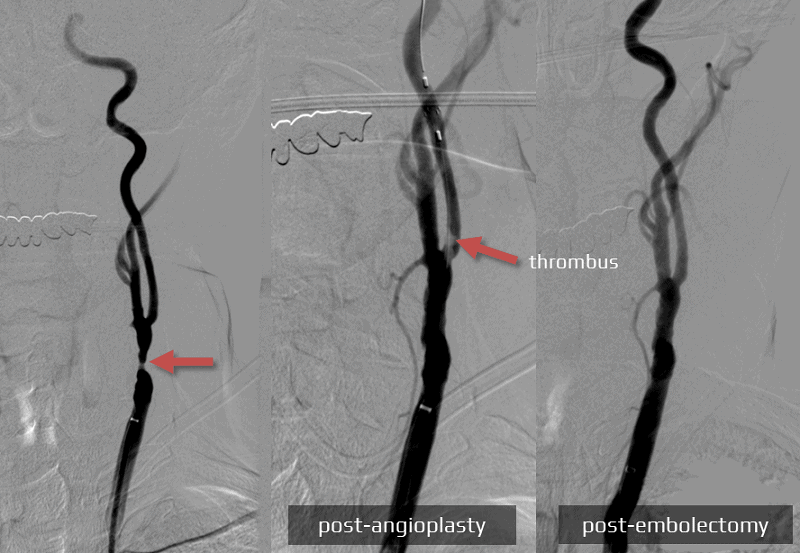
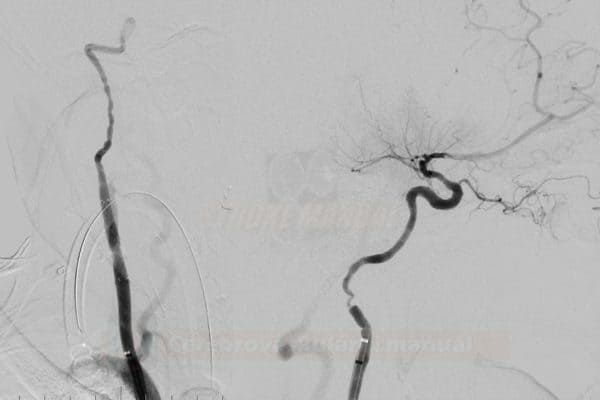
Artery thrombosis, distal thromboembolism
- microembolization x macroembolization
- separation of mural thrombus and plaque
- thrombus washout from the aneurysm sac, etc.
- minor embolizations may remain clinically silent
- the highest risk is observed during the procedure and within the following 72 hours
- dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is essential for stenting procedures
- mechanical thrombectomy and local thrombolytic therapy can be used to treat complications during DSA or recanalization procedures
- in cases of thromboembolic complications during aneurysm coiling after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), the successful use of IIb/IIIa inhibitors has been published [Aviv, 2005]
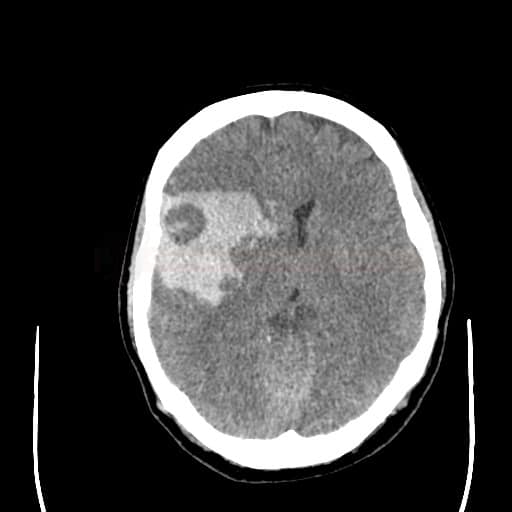
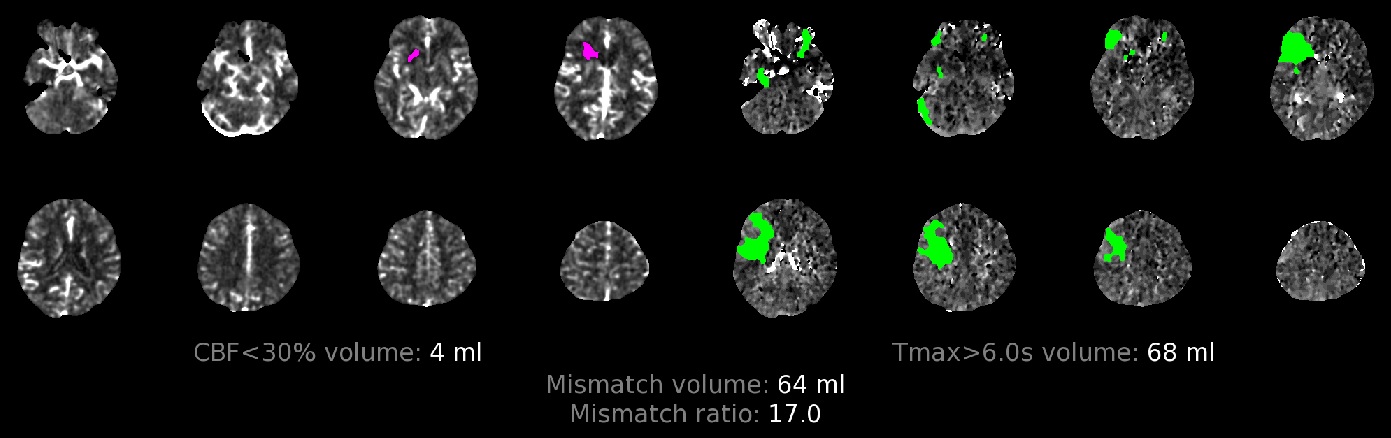
Hemorrhagic infarction
- bleeding most commonly occurs during reperfusion procedures in patients with concurrent extensive early ischemia (as indicated by low ASPECT score)
- petechial hemorrhage/parenchymal hematoma → classification of hemorrhagic complications
- hemorrhagic transformation of ischemia may be associated with intraventricular bleeding or SAH
- clinically symptomatic x asymptomatic
- if detected, neutralize heparin → see here
- in patients on DAPT (dual antiplatelet therapy) or patients treated with an IIb/IIIa inhibitor, give platelets and SOLUMEDROL 25 mg IV (if the patient is on clopidogrel) [Qureshi, 2008] → neutralizing effect of antiplatelet therapy
Vasospasms
- most vasospasms are transient and resolve after catheter removal
- more common in young individuals
- symptomatic x asymptomatic
- if a hemodynamically significant vasospasm persists, percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) may be performed and/or vasodilators (IA or IV) may be administered
(Dilceren / Nimotop) usually 1 mL/0.2 mg
- IV: 1-2 mg/h (5-10mL/h) by continuous infusion + 10 ml/h NS concomitantly
- AEs: hypotension, tachycardia
- combine with vasopressors in case of hypotension
- parenteral administration is not more effective than oral administration in preventing vasospasm
- infusion pumps with polyethylene tubing and needles with polyethylene handles (or all-metal) must be used, infusion solution is light sensitive, must not be used in direct sunlight
- IA: 50 mL (10mg) + 50mL NS (to get 10% solution; 10mL containing 1mg) … IA infusion 1mL/min (0.1mg /min)
-
0.5-2 mg into a single artery, total max dose 5 mg [Kim,2009]
-
(Verapamil / Isoptin / Lekoptin) usually 1mL/2.5 mg
- IA: bolus 1-3 mg (or 44 μg/kg) locally [Feng,2002]
- AEs: hypotension, bradycardia
(Perlinganit)
- IA: 0.5-2 mg as a slow bolus
(Asicord / Primacor)
- IA: 1mg/ml – 0.25 mg/min – infused for 30 minutes
- regression of vasospasm with combined IA and subsequent IV administration has been reported [Arakawa, 2001] [Fraticelli, 2008]
- IV administration alone seems to be effective [Crespy, 2019]
(Magnesium sulfate) usually 1mL/40 mg or 1mL/80mg
- IA: 10mL (1g) + 28 mL NS …. 0.25-1 g per artery [Shah, 2009]
- may be used in combination with nicardipine (2.5-20.0 mg/h for 30-60 min)
- magnesium is believed to inhibit cerebral vasospasm by causing smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation by mechanisms similar to the calcium channel antagonists
- IV: a large phase III study showed no significant benefit in cerebral vasospasm prevention or improved favorable outcomes when administered via IV infusion (Wong, 2010)
(Papaverine hydrochloride) 1mL/30mg
- IA: 300mg (10 mL) + 100mL of NS (solution concentration is < 3mg/mL) …. IA infusion 3mL/min for 30 minutes or 1.3 mL/min for 60 minutes [Kassel, 1992][Clouston, 1995]
- usually not used due to AEs
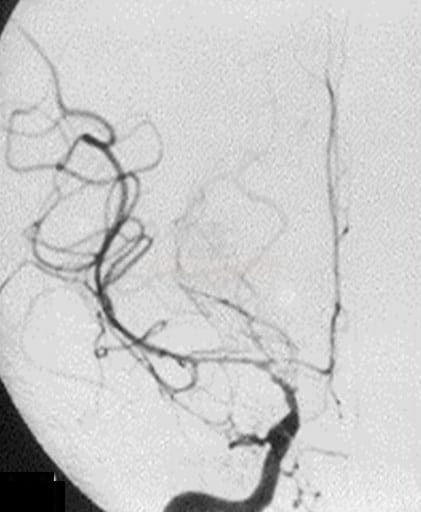
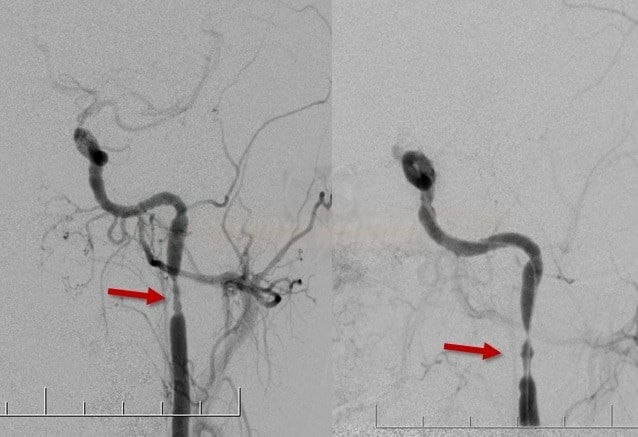
Arterial dissection/perforation
- dissection and pseudoaneurysm
- small dissections without thrombosis ⇒ observe
- consider the use of abciximab for small dissections associated with significant thrombosis
- symptomatic dissection may require acute stenting
- consider intervention for hemodynamically significant dissection (TIMI 0-1) (extracranial arteries)
- arterial rupture/perforation ⇒ SAH/ICH
- immediate endovascular intervention or surgery is required
- neutralize heparin → see here
- administer platelets (reverses the effect of antiplatelet therapy)
- bleeding after stenting poses a problem – stopping the bleeding increases the risk of stent thrombosis
- immediate endovascular intervention or surgery is required
Stenting-related complications
Peripheral (access-site) complications of endovascular procedures
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |
Systemic complications
Complications related to contrast media
Hemodynamic instability with hypoperfusion
- hemodynamic depression has been reported after both carotid artery stenting (CAS) and carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
- bradycardia with hypotension is usually a consequence of carotid sinus manipulation (parasympathetic activation)
- severe bradycardia ⇒ administer 0.5 mg IV bolus
- ATROPIN can also be used prophylactically in the following cases:
- severely calcified stenoses
- lesions in the carotid bulb
- history of myocardial infarction
- ATROPIN can also be used prophylactically in the following cases:
- moderate-severe hypotension ⇒ consider vasopressors + fluids