GENERAL MEDICINE
Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
Updated on 19/06/2024, published on 22/02/2022
- deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in veins. It most commonly occurs in the deep veins of the calf or thigh but can also appear in other parts of the body (such as the deep pelvic veins, veins in the abdomen, or arms)
- immobility increases the risk of DVT
- without prevention, DVT is detected in the first two weeks in up to 50% of immobile patients [Brandstater, 1992]
- thrombi form in the paretic leg and/or the pelvic veins
- approx. 2/3 of thrombi occur below the knee and are often asymptomatic, though there is a risk of proximal thrombus extension
- most symptomatic DVTs are located proximally (thigh, pelvis)
- most DVTs occur between days 3-7
- the most feared complication is pulmonary embolism (PE)
- incidence ~1% in 2 weeks [IST trial, 1997]
- PE accounts for up to 25% of deaths in stroke patients [Kelly, 2001]
- in bedridden patients, regular calf examinations are advisable (for swelling and palpation pain); nonetheless, many thromboses remain asymptomatic
- recommended VTE prophylaxis:
- mechanical prophylaxis is essential: IPC (intermittent pneumatic compression)
- medication: Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) or Unfractionated Heparin (UFH) (according to AHA/ASA 2019, the benefit is not sufficiently established – IIb/A)
Mechanical prophylaxis
- early physical therapy and verticalization
- intermittent pneumatic compression – IPC (e.g., Venaflow, Kendall, etc.) (AHA/ASA 2019 I/B-R)
- the effect of IPC and LMWH is comparable [Wan, 2015]
- the CLOTS 3 trial showed a reduction in 30-day mortality (13.1⇒10.8%) and incidence of DVT (12.1%⇒8.5%); in this study, a proportion of patients in both arms had LMWHs as well
- IPC should be interrupted for as short time as possible (skin hygiene, physical therapy) ⇒ IPC is designed for continuous use (CLOTS 3)
- do not use elastic compression stockings
Anticoagulants
- in general, the benefit of prophylactic administration of subcutaneous heparin (UFH or LMWH) in patients with acute stroke is not well established (AHA/ASA 2019 IIb/A)
- there were no significant effects on death or disability for LMWH compared with UFH
- LMWH was associated with a statistically significant reduction in mostly asymptomatic DVTs
- in routine practice, medical prophylaxis is used; according to data from the PREVAIL trial, enoxaparin 40 mg 1xd may be preferred to heparin 2x 5000 IU given its better clinical benefits-to-risk ratio and convenience of once-daily administration [Sherman, 2007]
According to the AHA/ASA guidelines 2019, IPC is the preferred prophylactic method.
The most effective approach is a combination of LMWH and IPC (Wan, 2015)
How to proceed in different types of stroke
Ischemic stroke
|
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
Intracerebral hemorrhage (AHA/ASA guidelines 2022)
|
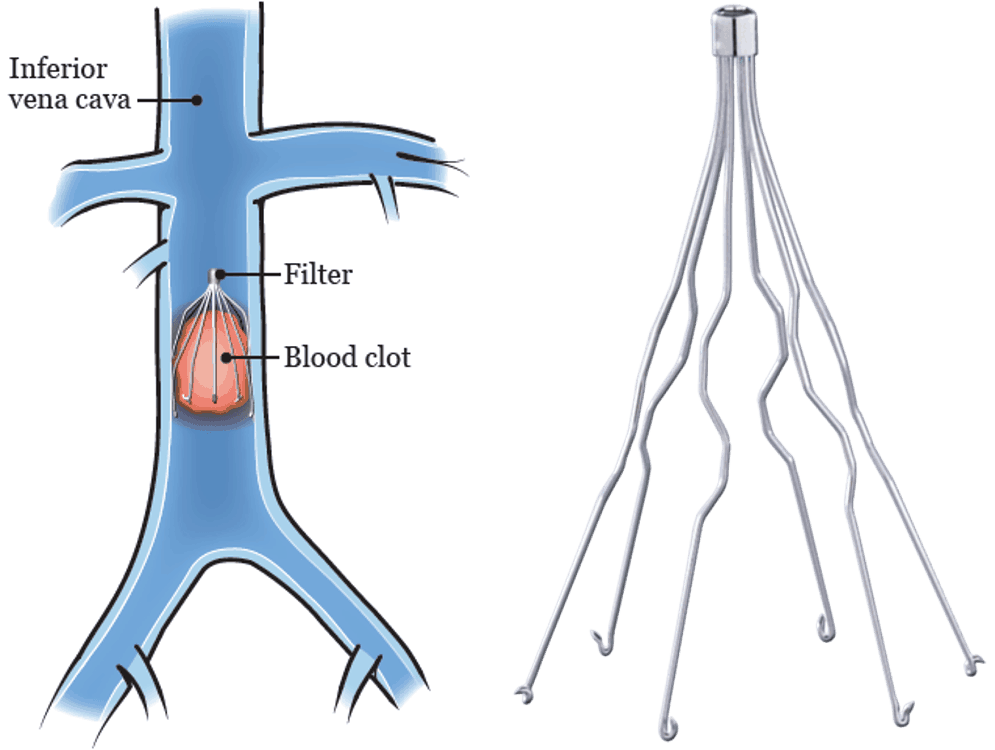
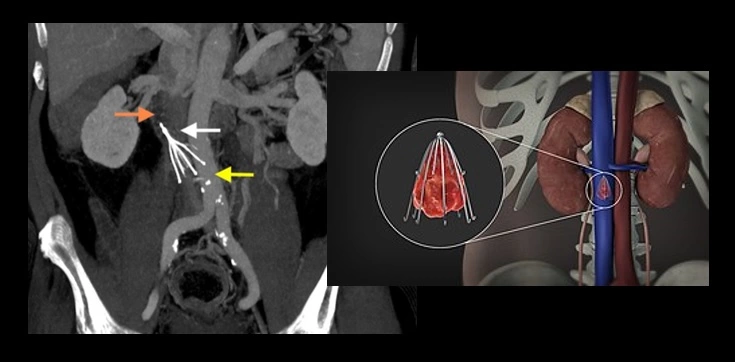
Consider implantation of Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) filter in SAH or ICH patients with acute PE or DVT (AHA/ASA 2010 class IIb, LoE C)