ISCHEMIC STROKE / CLASSIFICATION AND ETIOPATHOGENESIS
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Updated on 14/01/2024, published on 09/05/2023
Definition and pathophysiology
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a heterogeneous group of inherited connective tissue disorders characterized by hyperelastic skin, hypermobile joints, and vascular and other tissue fragility
- defects in connective tissue cause the signs and symptoms, which range from mild joint hypermobility to life-threatening complications
- the 2017 classification describes 13 distinct EDS subtypes (Malfait, 2017)
- inheritance pattern varies by EDS subtype
- mutations in at least 20 genes have been identified (e.g., COL5A1 or COL5A2 mutations cause the classical type of EDS)
- stroke is most commonly associated with type 4 (vascular EDS), characterized by an AD inheritance and abnormal production of type I and III procollagen due to mutations in the COL3A1 gene
- some genes associated with recently described types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome exhibit functions that seem unrelated to collagen
- prevalence of all EDS types is ~ 1 in 5000 individuals worldwide
- hypermobile and classic forms (types 1 and 5) are the most common
- most types are rare, often with only a few cases or families described in the literature
- incidence of vascular pathologies tends to increase with age [Pepin, 2000]
- most deaths in EDS result from arterial rupture
Clinical presentation
Dissection, aneurysm formation
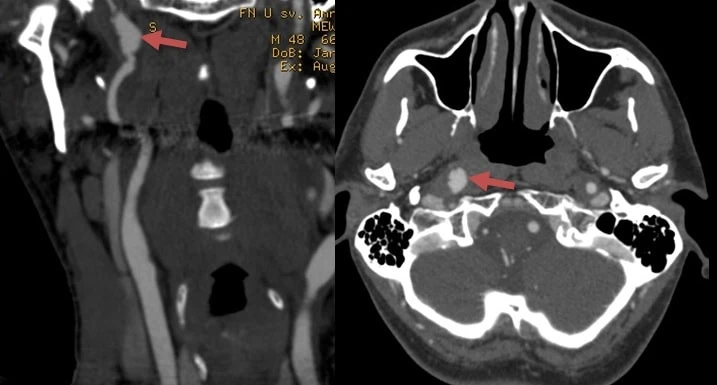
- increased risk of cerebrovascular events is particularly associated with the vascular subtype (vEDS)
- dissections primarily affect the carotid arteries and ascending aorta
- dissection may lead to ischemic stroke or SAH (intracranial dissection)
- aneurysms may be multiple; their rupture may lead to CCF formation, SAH, or ICH
Carotid-cavernous fistula
- carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) typically occurs spontaneously or following head trauma (Jindal, 2005)
- most CCFs are direct and result from the rupture of the ICA into the cavernous sinus
- the bilateral lesion is not uncommon
- CCF can be visualized by noninvasive vascular imaging, such as magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA)
- therapy: embolization, balloon occlusion
Diagnostic evaluation
- typical clinical presentation
- positive family history
- genetic testing
- the panel should include at least the COL5A1, COL5A2, COL1A1, and COL1A2 genes
- if genetic testing is unavailable, electron microscopy (EM) findings can support the clinical diagnosis
- abnormalities in collagen fibril architecture – irregular fibril diameter, disorganized arrangement, or abnormal interfibrillar spacing
- vascular imaging – preferably CTA, MRA
| clinical subtype | abbreviation | IP | protein | |
| 1 | Classical EDS | cEDS | AD | type I and V collagen |
| 2 | Classical-like EDS | clEDS | AR | tenascin XB |
| 3 | Cardiac-valvular | cvEDS | AR | type I collagen |
| 4 | Vascular EDS | vEDS | AD (COL3A1) | type I and III collagen |
| 5 | Hypermobile EDS | hEDS | AD | unknown |
| 6 | Arthrochalasia EDS | aEDS | AD | type I collagen |
| 7 | Dermatosparaxis EDS | dEDS | AR | ADAMTS-2 |
| 8 | Kyphoscoliotic EDS | kEDS | AR | FKBP22 and LH1 |
| 9 | Brittle Cornea syndrome | BCS | AR | ZNF469 |
| 10 | Spondylodysplastic EDS | spEDS | AR | β4GalT7 β3GalT6 ZIP13 |
| 11 | Musculocontractural EDS (myopatic) |
mcEDS | AR | D4ST1 DSE |
| 12 | Myopathic EDS | mEDS | AD or AR | type XII collagen |
| 13 | Periodontal EDS | pEDS | AD | C1r or C1s |
- major criteria
- generalized joint hypermobility (GJH)
- skin hyperextensibility and atrophic scarring
- minor criteria
- easy bruising
- soft, doughy skin
- skin fragility (or traumatic splitting)
- molluscoid pseudotumors
- subcutaneous spheroids
- hernia (or history thereof)
- epicanthal folds
- complications of joint hypermobility (e.g., sprains, luxation/subluxation, pain, flexible flatfoot)
- family history of a first-degree relative meeting clinical criteria
Minimal criteria suggestive of cEDS:
skin hyperextensibility and atrophic scarring
+
generalized joint hypermobility (GJH) and/or at least 3 minor criteria
Management
- acute stroke therapy
- standard stroke protocols and IVT contraindications apply; extra caution is required due to increased risk of bleeding
- experience with mechanical thrombectomy is limited; an increased risk of periprocedural arterial injury can be expected
- stroke prevention
- blood pressure control to reduce arterial wall stress
- antiplatelet agents are recommended for secondary prevention
- serial imaging studies for detection/follow-up of aneurysms or dissections
- symptomatic therapy
- pain anagement (analgesics, neuropathic agents like gabapentin)
- physical therapy should focus on joint stabilization and muscle strengthening
- orthotic support
- cardiovascular monitoring
- genetic counseling
- surgical interventions are generally reserved for life-threatening situations or severe mechanical dysfunction
FAQs
- EDS is a heterogeneous group of inherited connective tissue disorders characterized by hyperelastic skin, hypermobile joints, and vascular and tissue fragility
- EDS is caused by mutations in genes responsible for collagen production, a crucial protein for connective tissue strength and integrity
- mutations in at least 20 genes have been identified (e.g., COL5A1 or COL5A2 mutations cause the classical type)
- stroke is most commonly associated with type 4 (vascular EDS) with AD inheritance and abnormal type I and III procollagen production (COL3A1gene)
- yes, EDS is often inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner
- complications include joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, and, in severe cases, life-threatening cardiovascular conditions (arterial dissection, aneurysm rupture, stroke)
- with proper management, many individuals with EDS can lead active and fulfilling lives, though some may face challenges due to chronic pain or mobility issues
- currently, there’s no cure, but treatment can manage symptoms and prevent complications
- the overall life expectancy of patients with vascular EDS is shortened, largely as a result of vascular rupture, with a median life span of 48 years (range, 6–73 years)