ADD-ONS
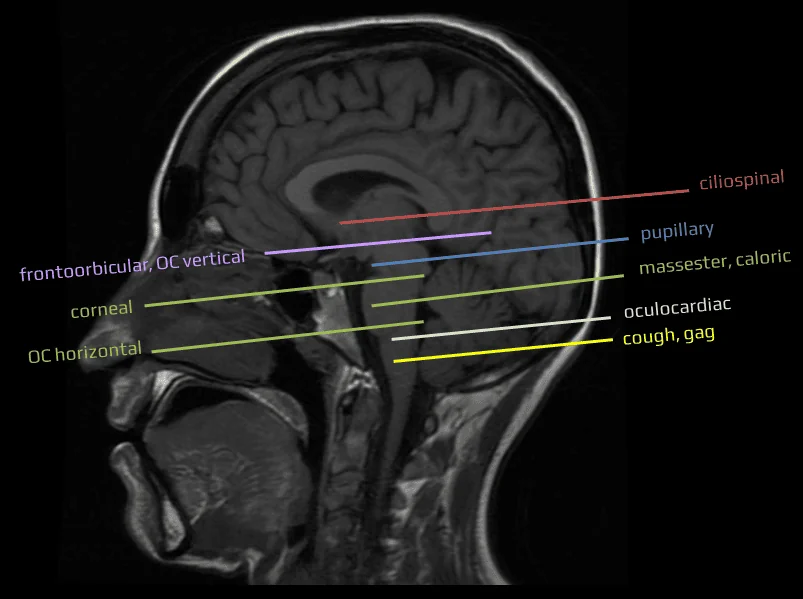
Brainstem reflexes
Updated on 22/06/2024, published on 11/04/2023
- brainstem (brain stem) reflexes are involuntary motor responses originating in the brainstem
- these reflexes are mediated by neural circuits that bypass higher cortical centers, enabling rapid, automatic responses
- clinically, they are used to:
- assess the integrity of the brainstem and cranial nerves
- evaluate the level of rostrocaudal deterioration
- detect brainstem death (as part of brain death protocol)
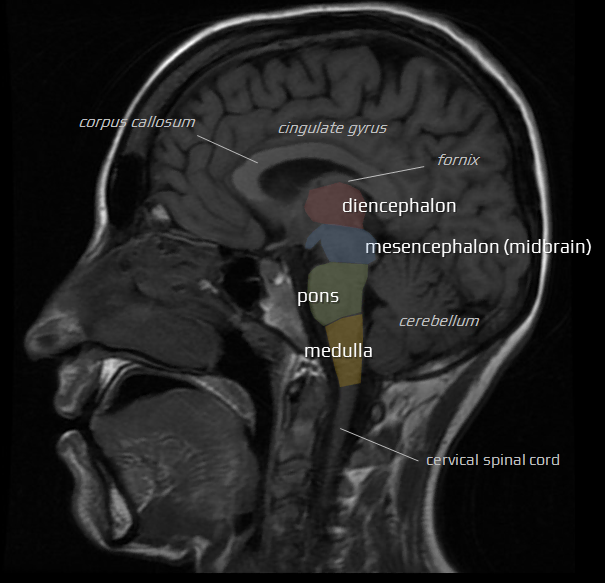
Diencephalic level
Painful stimulus is applied to the neck, face, or upper trunk → rapid ipsilateral pupil dilation (typically 1-2mm from baseline)
The ciliospinal reflex, mediated by the sympathetic nervous system, is regulated by the ciliospinal center in the spinal cord. Stimulation of this center results in pupil dilation on the same side as the stimulus
- dilation is relatively mild (1-2 mm) and should be checked with a magnifying glass for accuracy
- the reflex is extinguished in lesions of the brainstem, cervical spinal cord, and in lesions of the preganglionic and postganglionic fibers ⇒ areflexia has limited utility in topical diagnoses
- the reflex may help differentiate lesions at the cortico-subcortical and diencephalic levels
- if preserved, the disturbance of consciousness is likely caused by a lesion at the cortico-subcortical level
- if the reflex is absent while other brainstem reflexes are preserved, the lesion likely extends to the diencephalic level
- other factors influencing CS reflex:
- reflex is mediated by the cervical sympathetic fibers and is thus absent in Horner syndrome
- reflex is also absent during propofol-induced anesthesia
- enhanced ciliospinal reflex is observed in patients with cluster headache
- persistence of the ciliospinal reflex after cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a favorable prognostic sign for regaining consciousness
Pathway of the sympathetic innervation of the pupil
The sympathetic efferent pathway has three neurons and is ipsilateral
-
The first (central) neuron arises from the posterior hypothalamus and descends through the brainstem on the same side, close to the trigeminal nucleus. It descends dorsally and rostrally to the red nucleus and lies at the lateral tegmentum of the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It synapses at the ciliospinal center of Budge, located at C8 to T2 in the intermediolateral (IML) horn of the gray matter of the spinal cord.
-
The second (preganglionic) neuron originates from the ciliospinal center and goes to the superior cervical ganglion in the neck. It exits the spinal cord through the dorsal spinal root and enters the paravertebral sympathetic chain. The second-order neuron passes near the apex of the lung and may suffer damage in surgeries of the neck or bronchogenic carcinoma (Pancoast tumor), causing Horner’s syndrome.
-
The third (postganglionic) neuron passes on the surface of the internal carotid artery and joins the ophthalmic nerve at the cavernous sinus. The sympathetic postganglionic fibers pass through the nasociliary nerve and long ciliary nerve and reach the ciliary body and the dilator pupillae muscles
Diencephalic-mesencephalic level
also known as the frontalis-orbicularis oculi reflex or forehead-eyelid reflex
Tapping the glabella and the supraorbital arches → bilateral contraction of the upper parts of the orbicularis oculi muscles (winking)
- the reflex has two integral components:
- early – an exteroceptive oligosynaptic trigeminofacial reflex with its center in the upper pons
- late – a nociceptive multisynaptic reflex integrated within the meso-diencephalic reticular formation (RF)
- the reflex is normally habituated through repeated stimulation (known as extinction phenomenon)
- abnormal response:
- in patients with cortical impairment, the reflex is not habituated due to a disturbance in the cortical inhibitory mechanisms
- minimal unilateral contraction indicates an incomplete lesion of the diencephalic-mesencephalic RF
- reflex is influenced by sedatives
- reflex is absent in lesions at the diencephalic-mesencephalic junction
Diencephalic-mesencephalic level
Repeated anteflexion-retroflection movements of the patient’s head → a conjugate movement of the eyeballs in the opposite direction (baby-doll response)
- vertical and horizontal oculocephalic reflexes (doll’s eyes reflex) are using the vestibular-ocular reflex (VOR) for neurologic examination of cranial nerves III, VI, and VIII
- vestibulo-proprioceptive-oculomotor reflex helps:
- test for oculomotor paralysis in unconscious patients
- assess the level of brainstem functional transsection (level of rostrocaudal deterioration)
- absent in conscious persons (inhibited by visual cortical centers)
- vertical deviation of at least one eyeball indicates the presence of the reflex
- usually, only head retroflexion is tested (repeated anteflexion may increase the risk of herniation)
- upward movement can be tested by the corneal reflex (Bell’s phenomenon)
- reflex is absent in lesions at the diencephalic-mesencephalic junction ⇒ dissociation of the oculocephalic reflexes (vertical absent, horizontal present)
- this reflex is also affected by lesions of the vestibulo-ocular structures
Mesencephalic-pontine level (middle mesencephalon)
- the pupillary light reflex (PLR) regulates pupil diameter in response to the intensity of light reaching the retina
- unilateral illumination triggers pupil constriction in both eyes
- direct response – miosis (constriction) of the illuminated pupil
- consensual response – miosis of the contralateral pupil
- optic nerve lesion: direct and indirect responses are absent if the affected eye is illuminated
- oculomotor nerve lesion: illumination of the damaged side induces only a consensual reaction; the direct reaction is absent due to the damage of efferent pathways. Illumination of the healthy eye induces only a direct reaction
- brainstem death: the pupillary reaction is absent in both eyes
Mesencephalic-pontine level (upper pons)
Touching the cornea from the side (to eliminate blink reaction triggered by the optic nerve) → bilateral eyelid closure and Bell’s phenomenon (elevation and slight abduction of the eyeballs)
- the intensity of the evoking stimulus must be proportional to the subject’s level of consciousness.
- a gentle touch to the cornea for a fully conscious person
- stronger or repeated stimulation for someone in a coma
- a nociceptive polysynaptic reflex involves the trigeminal nerve as the afferent pathway and facial and oculomotor nerves as the efferent pathways
- the afferent part of the reflex arc has synapses with the bulbar and pontine nuclei of the trigeminal nerve
- corneal reflex is altered by pontine lesions or lesions of CN V and VII
- severe weakness of the orbicularis oculi muscle or ocular pathology must be ruled out when assessing this reflex
- severe weakness of the orbicularis oculi muscle or ocular pathology must be ruled out when assessing this reflex
Mesencephalic-pontine level (middle pons)
- the jaw reflex (jaw-jerk or masseter reflex) is a deep tendon reflex that involves the muscles of mastication, primarily the masseter muscle
- anatomy (trigemino-trigeminal reflex):
- sensory component: trigeminal nerve (CN V/3)
- motor component: trigeminal nerve (CN V/3)
- muscle tested: masseter
- testing: with the patient’s jaw slightly open, the reflex is elicited by tapping with a reflex hammer on the chin or on a tongue blade resting on the lower teeth
- the normal response: sudden stretching of the masseter muscle leads to its reflex contraction ⇒ the jaw moves upward
- abnormal responses:
- the reflex is extinguished in a primary pontine lesion or as a consequence of central rostrocaudal deterioration syndrome reaching the level of the upper pons (transsection)
- the reflex ceases in a deep coma due to muscular atonia
- an exaggerated jaw jerk (sometimes with clonus) implies a bilateral upper motor neuron lesion (e.g., in pseudobulbar palsy)
Mesencephalic-pontine level (middle pons)
- verify an intact external auditory canal and tympanic membrane via otoscopy
- position the patient’s head at a 20-30° anteflexion
- 10-30 mL of cold water is instilled into the external auditory canal (both sides should be tested separately, with a 5-minute interval between tests)
- observe eye movements for 1 minute
- the lateral semicircular canal is primarily stimulated, causing tonic conjugate deviation of the eyes toward the stimulated ear (nystagmus is absent in coma)
- in non-comatose individuals, nystagmus beating away from the stimulated ear is observed
- warm water induces the opposite deviation
- afferent pathway: vestibular nerve
- center: the vestibular and abducens nuclei in the pons, as well as oculomotor nuclei in the mesencephalon
- efferent pathway: oculomotor and abducens nerves, innervating the medial and lateral rectus muscles
Mesencephalic-pontine level (lower pons)
A reflex movement of the eyeballs in the direction opposite to the passive brisk rotation of the head. During the test, the patient’s eyelids are held open.
Avoid this test in patients with head or neck injuries!
This test examines the vestibulo-ocular reflex in the horizontal plane.
- intact CN III, VI, VIII, corresponding nuclei in the midbrain/pons, and the vestibular system
- suggests a lesion of the homolateral pontine or contralateral cortical visual center
- failure to elicit during 15 rotations indicates a large pontine lesion (either primary or secondary due to herniation)
- eyes remain in midline position during head rotation
- exclude the effects of barbiturates
- in conscious individuals, the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) reflex can be modulated and inhibited by the cerebral cortex
- frontal and parietal lobes exert influence over the VOR to enable more precise control of eye movements; this cortical modulation allows individuals to override or adjust the VOR when necessary
- when we intentionally shift our gaze or follow a moving object, the cortex can suppress the VOR to enable voluntary eye movements. This coordination between cortical processing and the VOR is essential for our ability to adapt our gaze and focus on specific objects or tasks, even when head movements are involved
- allows assessment of oculomotor disorders
- oculomotor nerve palsy: paresis of adduction with intact contralateral abduction
- internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO)
- impaired adduction of the ipsilateral eye with nystagmus in the abducting eye
- caused by a lesion of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)
- one-and-half syndrome
- combination of ipsilateral conjugate horizontal gaze palsy (one) and ipsilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) (a half)
- only a swaying abduction movement of one eye is present, while the contralateral eye is immobile
- the lesion typically involves the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF), abducens nucleus, and the ipsilateral medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)
- oculomotor nerve palsy: paresis of adduction with intact contralateral abduction
Ponto-bulbar level
The eyeball is compressed for 10-20 seconds; the test is positive if the pulse drops by > 8-10 beats per minute. The reflex tests the integrity of the caudal brainstem
- the response is maximal within the first 20 seconds and involves polysynaptic (trigeminovagal) reflex
- afferent part – trigeminal nerve (V1 branch)
- efferent part – vagal nerve
- the reflex may induce bradycardia and, in extreme cases, cardiac arrest
- when the bulbar level is reached during rostrocaudal deterioration syndrome in supratentorial lesions
- in primary caudal brainstem lesions
- in pontine lesions affecting bilateral trigeminal nuclei
- in orbital fracture or damage of the V1 branch of the trigeminal nerve
- the response is increased in hypercapnia and hypokalemia, and decreased following atropine administration
- traumatic orbital hemorrhage may cause homolateral mydriasis and bradycardia due to damage to the ciliary ganglion
Bulbar level
The test is performed through deep tracheal irritation or stimulation of the posterior pharyngeal wall or the laryngeal region using a soft-tip catheter.
An absent cough reflex suggests a lesion in the afferent or efferent pathways (involving the vagus and phrenic nerves) or the medullary centers. The response in brainstem death is the absence of a cough
- cough reflex is a complex physiological mechanism designed to protect the airways from aspiration and to facilitate the removal of mucus and foreign objects
- pathway: vagal nerve (sensory receptors, mainly in the larynx and tracheobronchial tree) – multiple nuclei in the medulla oblongata (the cough center) – vagal nerve
Bulbar level
An absent gag reflex suggests a lesion in the afferent or efferent pathways or the medullary centers. The response in brainstem death is the absence of a gag reflex
- the gag reflex (pharyngeal reflex) is a protective mechanism that helps prevent foreign objects from entering the throat
- anatomy involved:
- sensory component: glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and vagus nerve (CN X)
- motor component: vagus nerve (CN X)
- muscles: pharyngeal constrictors and levator veli palatini
- the examiner touches the posterior pharyngeal wall, tonsillar area, or base of the tongue with a tongue depressor or cotton-tipped applicator
- normal response involves contraction of the pharyngeal muscles, elevation of the soft palate, and retching or gagging sensation
- some individuals may have a very sensitive reflex, while others may have a diminished or absent reflex without any underlying pathology
- absent or diminished gag reflex may indicate:
- damage to CN IX or CN X
- pseudobulbar palsy
- brainstem lesions
| reflex | afferent pathway | center | efferent pathway |
| Ciliospinal (CS) | cervical pain fibers (neck) trigeminal nerve (face) |
spinal cord (intermediolateral column) |
sympathetic fibers |
| Pupillary | retina – optic nerve | pretectal nucleus, Edinger-Westphall nucleus | oculomotor nerve (miosis) |
| hypothalamus, cervical ganglion | sympathetic fibers (mydriasis) | ||
| Fronto-orbicular (nasopalpebral) |
trigeminal nerve (V1) | pons | facial nerve |
| Oculocephalic vertical | vestibulocochlear nerve | mesencephalon (midbrain) | oculomotor nerve |
| Corneal | trigeminal nerve (V1) | pons | facial nerve oculomotor nerve |
| Masseter (jaw jerk) |
trigeminal nerve (V3) | pons | trigeminal nerve (V3) |
| Vestibulo-ocular (caloric) reflex | vestibulocochlear nerve | mesencephalon pons |
oculomotor nerve abducent nerve |
| Oculocephalic horizontal | vestibulocochlear nerve | pons | oculomotor nerve abducent nerve |
| Oculocardiac | trigeminal nerve (V1) | pons medulla oblongata |
vagal nerve |
| Cough reflex | vagal nerve |
medulla oblongata | vagal nerve |
| Gag reflex |
glossopharyngeal nerve |
medulla oblongata | vagal nerve |