ADD-ONS / SCALES
The ARWMC Rating Scale
Updated on 22/03/2024, published on 25/04/2023
ARWMC (Age-Related White Matter Changes)
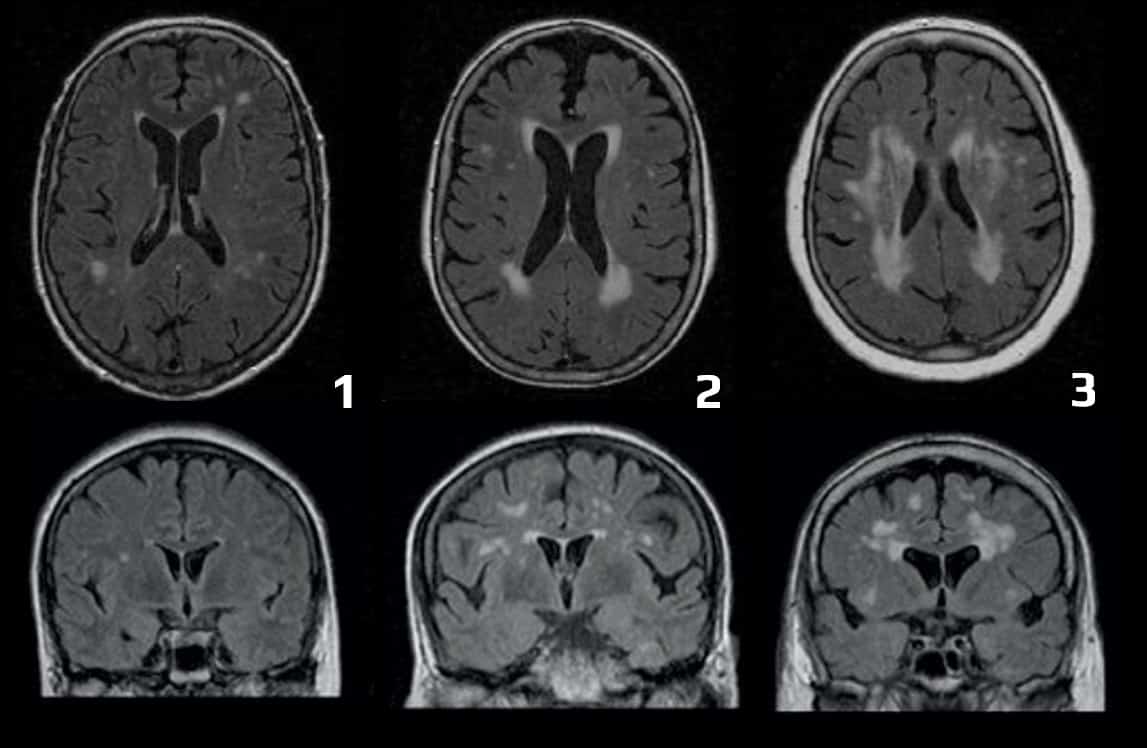
- this scale was designed to evaluate white matter changes (WMCs) on either CT or MRI scans
- sensitivity and reliability are higher with MRI
- differences between MRI and CT in the detection of WMCs are primarily related to lesion size – MRI is better at detecting small lesions, while medium and large lesions are equally well visualized by both modalities
- regional differences play a minor role, as ARWMC lesions occur in areas that can usually be imaged with high quality by both MRI and CT
- WMCs definition:
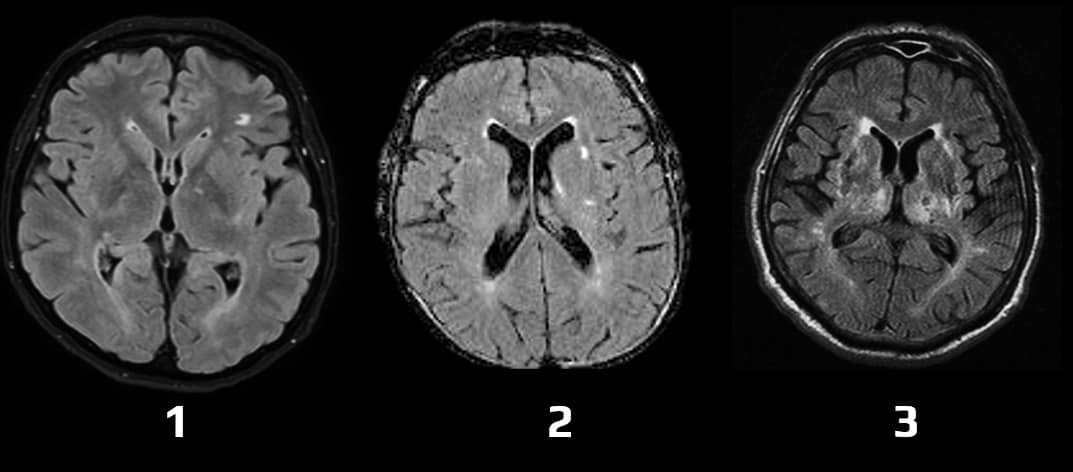
- T2 or FLAIR MRI images – bright (hyperintense) lesions ≥ 5 mm
- NCCT – hypodense areas ≥ 5 mm
- T2 or FLAIR MRI images – bright (hyperintense) lesions ≥ 5 mm
- the following areas are scored (each hemisphere separately):
- frontal
- parieto-occipital
- temporal
- infratentorial, including the cerebellum
- basal ganglia (striatum, globus pallidus, thalamus, internal and external capsule, and insula)
- FAZEKAS scale is easier to use in routine clinical practice
|
White matter lesions (WML)
|
|
| 0 | no lesion (including symmetrical, well-defined caps or bands) |
| 1 | focal lesions |
| 2 | an incipient confluence of lesions |
| 3 | diffuse involvement of the entire region, with or without U-fibers involvement |
| Basal ganglia lesions | |
| 0 | no lesion |
| 1 | 1 focal lesion (≥ 5 mm) |
| 2 | > 1 focal lesion |
| 3 | confluent lesions |