ISCHEMIC STROKE / ACUTE THERAPY
Sonothrombolysis
Updated on 06/11/2023, published on 09/09/2022
Introduction
- diagnostic ultrasound at high frequency (~2 MHz) and low intensity accelerates enzymatic processes induced by thrombolytics (a phenomenon known as sonothrombolysis). This can be applied externally using commercial transcranial and duplex Doppler devices
- it provides:
- improved penetration of fibrinolytic drugs into the thrombus
- direct activation of the fibrinolytic system
- change in thrombus microstructure and improved binding of thrombolytics to fibrin [Braaten 1997]
- low-frequency (300 kHz) transcranial ultrasound was also tested to accelerate thrombolysis; the TRUMBI trial was terminated prematurely due to high rates of intracranial bleeding [Daffertshoffer, 2007]
Methods
Sonothrombolysis
- the CLOTBUST trial demonstrated a higher rate of complete recanalization in patients treated with IVT combined with 2-hour TCD monitoring (2MHz probe) compared to IVT alone
[Alexandrov, 2004]]
- according to several in vitro and human clinical studies, the use of echo contrast during sonothrombolysis further augments its recanalization potential (DEFINITI, TUCSON )
- a significant obstacle to the further development of sonotrombolysis and initiating a large-scale clinical trial (that would have the power to demonstrate clinical effect) is the unavailability of experienced sonographers
- thus, an automated operator-independent device was developed
- the CLOTBUST-HF was a pilot trial with the CLOTBUST-ER device from Cerevast [Barreto, 2013]
- in 2015, the multicenter phase 3 CLOTBUST-ER trial was terminated prematurely due to negative results [Alexandrov, 2019]
- the CLOTBUST-HF was a pilot trial with the CLOTBUST-ER device from Cerevast [Barreto, 2013]
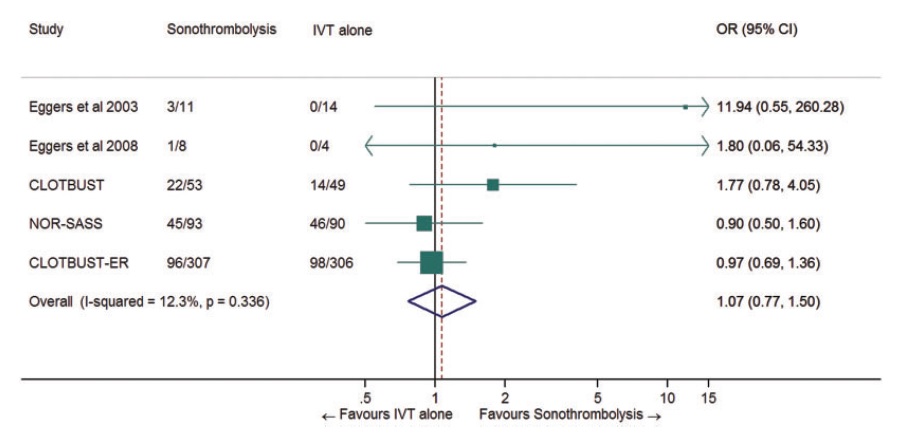
- a meta-analysis of 5 RCTs demonstrated no benefit (mRS score 0-1/3 months) of sonothrombolysis over TL alone
- sonothrombolysis is currently not recommended beyond clinical trials (ESO guidelines 2021) (AHA/ASA 2019 III/A)
Endovascular sonothrombolysis
- direct endovascular insonation of the thrombus using endovascular probes attached to the end of the catheter (e.g., EKOS system) was tested
- the IMS3 trial was terminated early in 2012 – no significant clinical benefit of combination therapy over IVT alone was demonstrated (Broderick, 2013)
Sonolysis
- small-scale trials testing the efficacy of standalone insonation without tPA (sonolysis) during interventional procedures (CEA, CAS) indicate potential for reducing thromboembolic risk → more here
| Content available only for logged-in subscribers (registration will be available soon) |