ADD-ONS / ANATOMY
Cerebral collateral circulation
Updated on 24/04/2024, published on 01/10/2023
- cerebral collateral circulation refers to a backup network of blood vessels that stabilizes cerebral blood flow when primary arteries supplying an area of the brain become stenosed or occluded
- hypoperfusion may be caused by atherosclerosis, embolism, hemodynamic compromise, or a combination of these factors
- reduced anterograde flow alters pressure gradients, leading to the opening (recruitment) of collateral vessels
- collateral vessels help maintain adequate blood supply to brain tissue; their quality significantly influences the severity and extent of cerebral infarction in the case of acute occlusion
- well-developed and functional collaterals can temporarily replace the function of the occluded artery, significantly improving the patient’s prognosis
- well-developed and functional collaterals can temporarily replace the function of the occluded artery, significantly improving the patient’s prognosis
Classification
Functional
Primary cerebral collateral system
- preexisting anastomoses that instantly redirect blood flow to the ischemic area
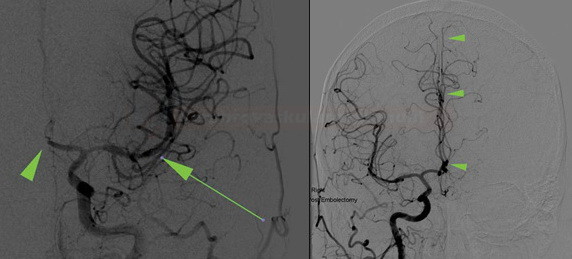
- arteries of the circle of Willis (e.g., ICA occlusion leads to reversed flow in AComA or PComA)
Secondary cerebral collateral system
- these collaterals take time to recruit and become fully functional
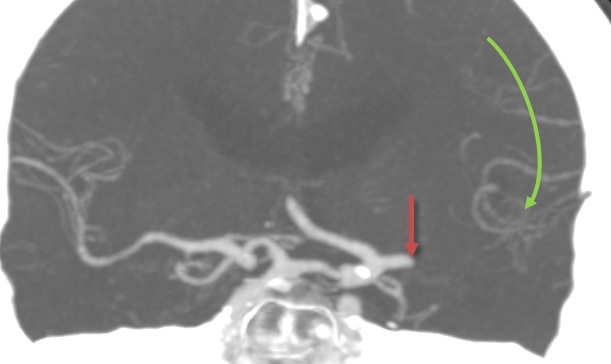
- the leptomeningeal anastomoses (LMAs) form a network of arterioles located in the pia mater, connecting the main cerebral arteries (ACA, MCA, PCA) and main branches of the MCA
Anatomic
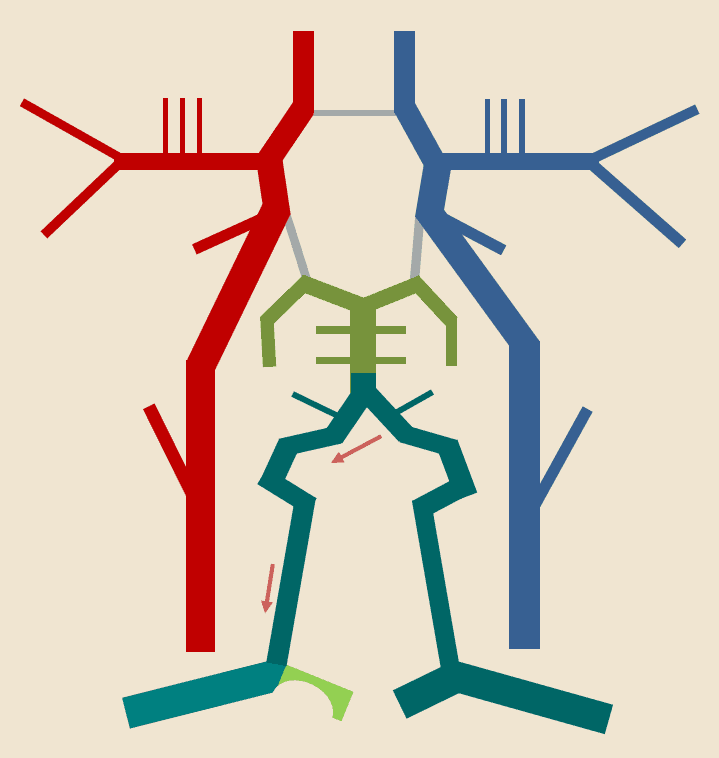
Extracranial collateral system
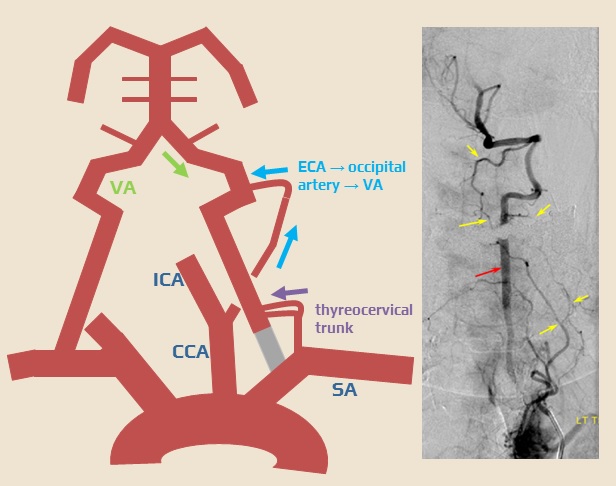
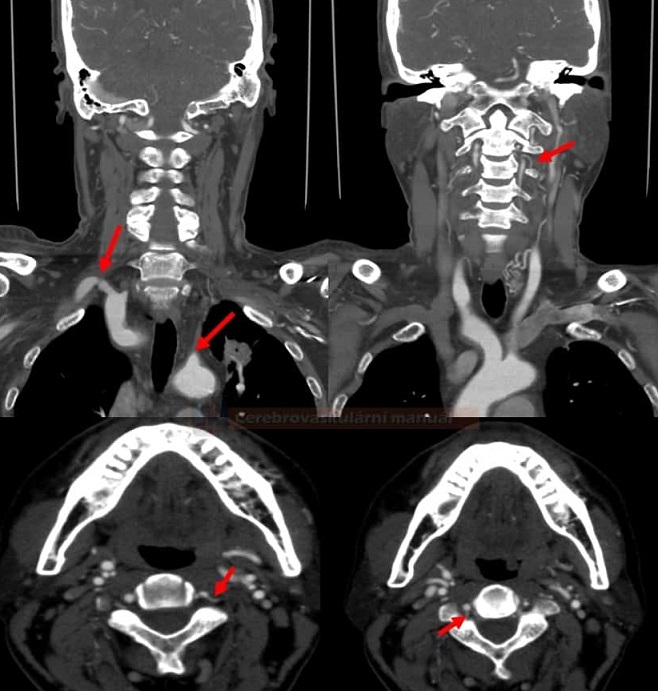
- subclavian artery → ECA (thyrocervical trunk, inferior and superior thyroid artery)
- subclavian artery → VA (thyrocervical trunk → muscular branches → VA)
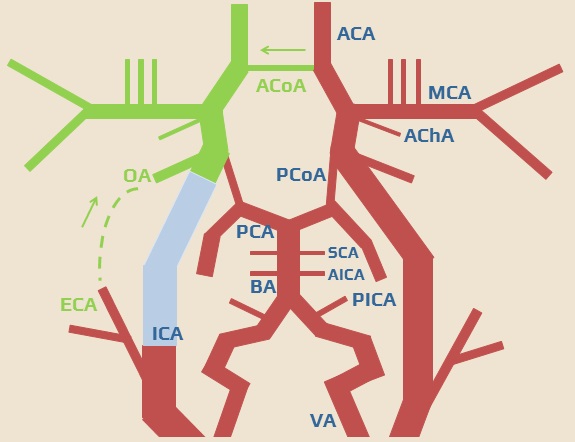
- ECA → ICA (facial/maxillary/superficial temporal artery → ophthalmic artery → carotid siphon)
- ICA → contralateral ICA (ACA → ACoA)
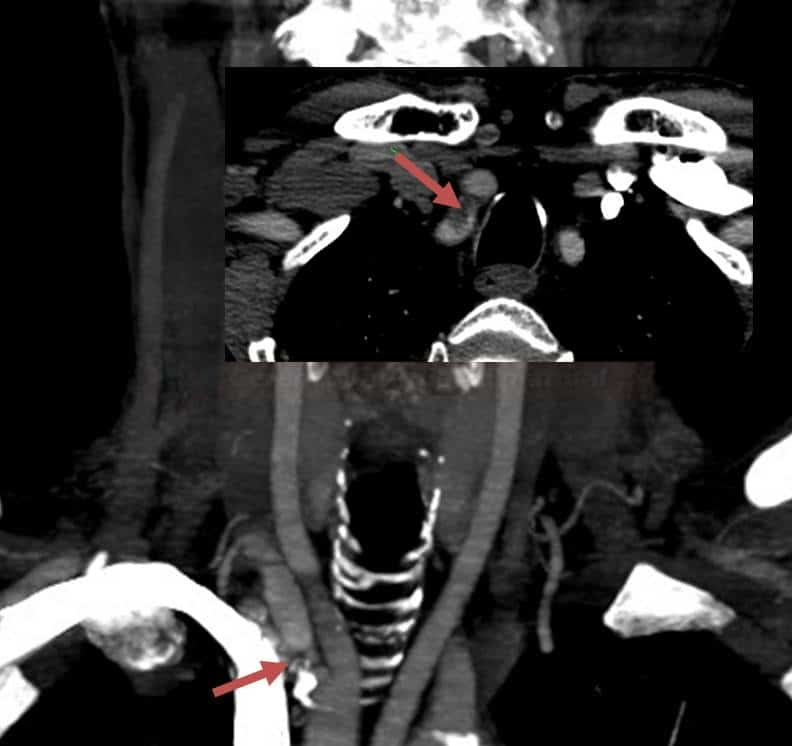
- ECA → VA (occipital artery → muscular branches → VA)
- ICA → posterior circulation
- ACA → pericallosal artery → PCA
- MCA → parietooccipital branches → PCA
- carotid siphon → PCoA → PCA
- carotid siphon → anterior choroid artery → posterior choroid artery → PCA
- carotid siphon → trigeminal artery → BA
- VA → contralateral VA (via spinal branches)
Intracranial collateral system
- circle of Willis (primary collaterals) – used in stenoses and occlusions of large arteries (CCA, ICA, VA)
- leptomeningeal anastomoses (LMA)
- end-to-end anastomoses of major cerebral arteries (MCA-ACA, MCA-PCA, ACA-PCA)
- play a crucial role in acute stroke due to occlusion of the artery forming the circle of Willis or in the peripheral segments
- other anastomoses
- tectal plexus connecting the supratentorial branches of the PCA with the infratentorial branches of the superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
- orbital plexus connecting the ophthalmic artery with the facial, maxillary, ethmoid, and middle meningeal arteries
- tectal plexus connecting the supratentorial branches of the PCA with the infratentorial branches of the superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
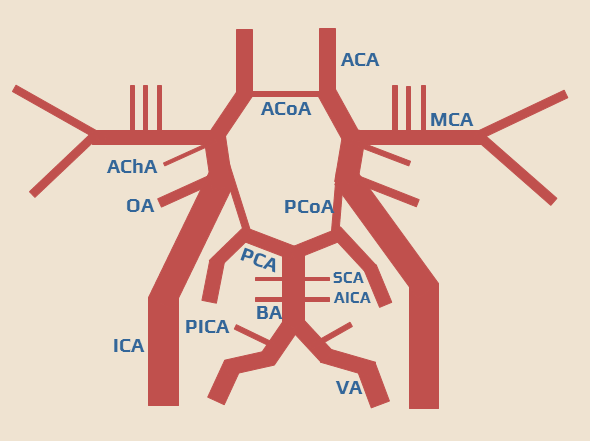
The circle of Willis
- intracranially, the basal arteries are interconnected to form the arterial circle of Willis
- it is a heptagon composed of the following components:
- left and right ICA
- left and right A1 segments, connected by an unpaired AComA
- left and right P1 segments
- left and right PComA (connecting the ICA and P1 segment on each side)
- PcomA originates at the anterior perforating substance and runs posteriorly through the interpeduncular cistern
- basilar artery tip
- branches of the circle of Willis also supply the optic chiasm and tracts, infundibulum, hypothalamus, and other structures at the base of the brain
- medial lenticulostriate arteries (from segment A1)
- perforating branches (from the AComA)
- thalamoperforating and thalamogeniculate arteries (from the basilar tip, proximal PCA, and PComA)
- the circle of Willis allows for the redirection of blood flow between both hemispheres and between the vertebrobasilar and carotid circulations
- a complete circle is present in < 30% of patients; individual anatomical variants are common
- different diameters of vessels on the right and left side
- predominance of carotid or vertebral blood flow
- significant asymmetry of the entire circuit
- absence/hypoplasia of one of the arteries
- AComA (~ 1%)
- proximal segment of the ACA (~ 10%)
- absent or hypoplastic PComA (~ 30%)
- AComA (~ 1%)
Leptomeningeal anastomoses (LMAs)
- leptomeningeal anastomoses refer to the collateral vascular network within the pia mater
- they serve as alternative pathways for cerebral blood flow
- typically, they are formed by end-to-end anastomoses between the ACA-MCA, ACA-PCA, and MCA-PCA; anastomoses also exist between both ACAs
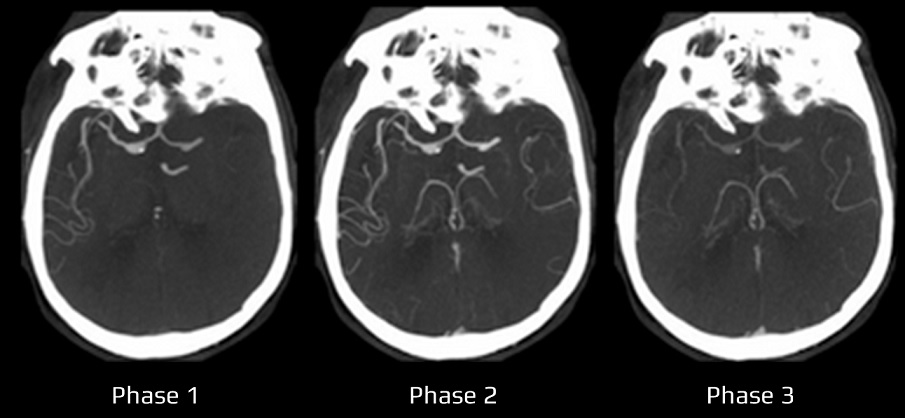
- occlusion of a cerebral artery leads to hypoperfusion in the corresponding vascular territory. This generates a pressure gradient between vessels in the unaffected area and the territory of the stenotic/occluded artery, resulting in retrograde filling of the affected area
Factors affecting LMAs functionality
- inter-individual anatomic variability in the number and extent of LMAs ⇒ LMA functionality and compensatory abilities significantly influence the prognosis of patients with acute stroke
- blood pressure – the pressure gradient depends on systemic blood pressure; therefore, only extreme BP values require correction in acute stroke patients → see here
- occlusion dynamics
- in progressive stenosis leading to occlusion, LMAs develop gradually, increasing their compensatory capacity over time
- with sudden occlusion, the compensatory mechanisms are unable to respond rapidly
- in progressive stenosis leading to occlusion, LMAs develop gradually, increasing their compensatory capacity over time
- the patient’s age – the compensatory capacity of the LMA is generally reduced in the elderly. In some cases, preexisting chronic proximal stenosis may have helped to establish adequate collaterals
Assessment of collateral circulation
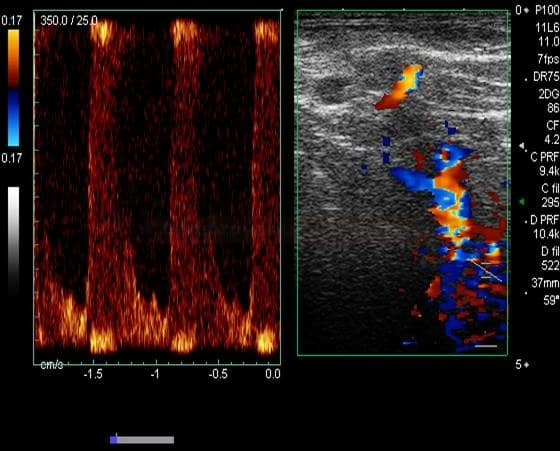
Neurosonology
- detection of extracranial shunts (mainly reverse flow in the ophthalmic artery) or detection of collaterals supplying distal portions of the vertebral artery in proximal occlusion/stenosis
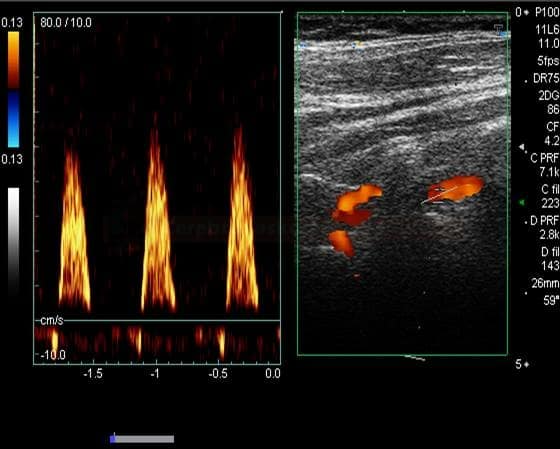
- detection of subclavian steal syndrome caused by stenosis/occlusion of the subclavian artery
- assessment of collateral circulation within the Circle of Willis (reversed flow in ACoA or PCoA) + assessment of flow in collaterals (peak systolic velocity and systolic acceleration in affected arteries)
- the ability of repeated flow monitoring is a significant advantage → information on intracranial dynamics can help to decide on further management
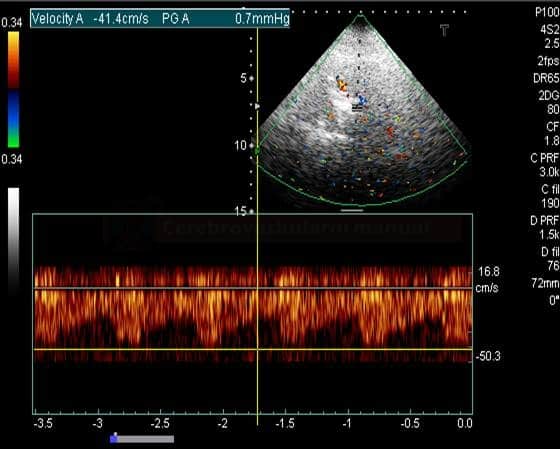
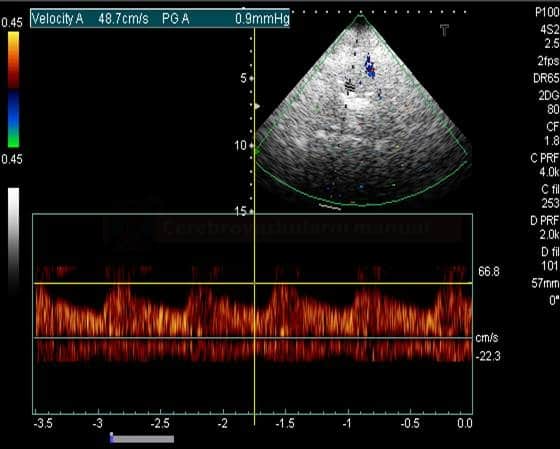
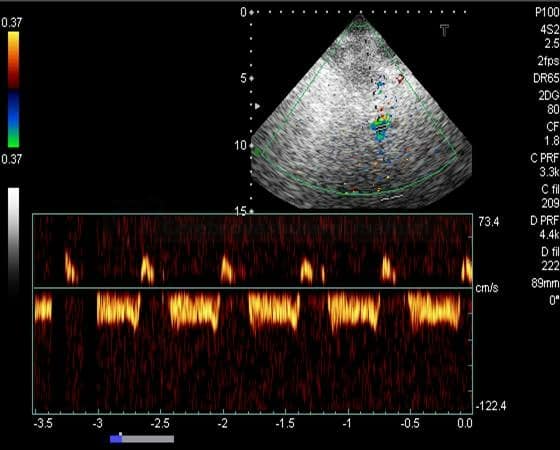
THE STEAL PHENOMENON IN A PATIENT WITH RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY STENOSIS

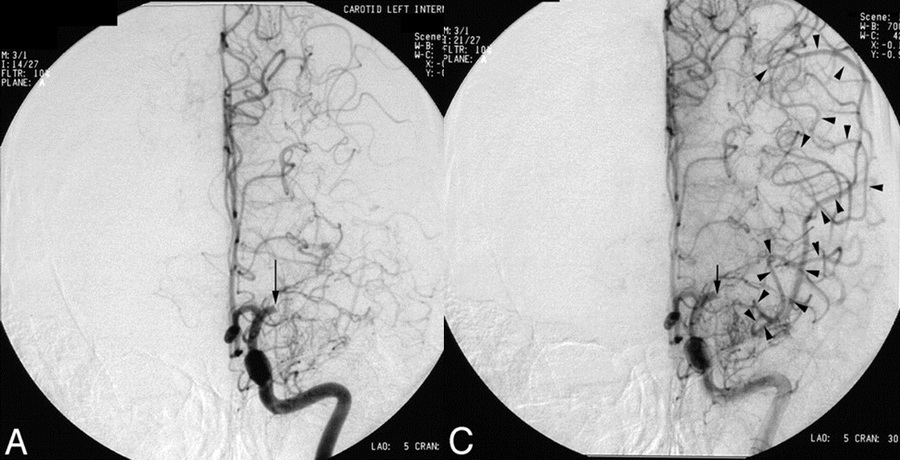

![a - PCA, b - LMAs between MCA-ACA, c - LMAs between PCA-MCA, d - tectal plexus between PCA-SCA, e - distal cerbellar artery anastomoses f - ACoA [Liebeskind, 2003] a - PCA, b - LMAs between MCA-ACA, c - LMAs between PCA-MCA, d - tectal plexus between PCA-SCA, e - distal cerbellar artery anastomoses f - ACoA [Liebeskind, 2003]](https://www.stroke-manual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/collaterals-e1646128709696.png)